Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackReview of Aerobic Cellular Respiration definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
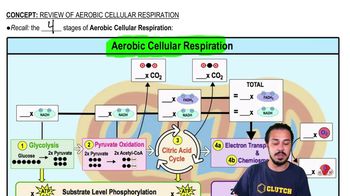
- GlycolysisThe first stage of aerobic respiration, breaking down glucose into 2 pyruvates, producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
- Pyruvate OxidationConverts pyruvates into acetyl CoA, yielding 2 NADH and releasing 2 CO2.
- Krebs CycleA cycle that generates 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2, releasing 4 CO2 from acetyl CoA.
- Oxidative PhosphorylationFinal stage producing 26-34 ATP and water, using electron carriers in the electron transport chain.
- MitochondriaThe organelle where the majority of aerobic cellular respiration occurs.
- CytoplasmThe cell area where glycolysis occurs, outside the mitochondria.
- Electron Transport ChainA series of complexes that transfer electrons, building a hydrogen ion gradient for ATP production.
- ChemiosmosisThe process of ATP generation using a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane.
- NADHAn electron carrier produced in glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the Krebs cycle.
- FADH2An electron carrier produced in the Krebs cycle, used in oxidative phosphorylation.
- Acetyl CoAA molecule formed from pyruvate, entering the Krebs cycle for further energy extraction.
- Substrate Level PhosphorylationA method of ATP production occurring in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
- Carbon DioxideA waste product released during pyruvate oxidation and the Krebs cycle.
- WaterA product formed when oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
- ATPThe main energy currency of the cell, produced in various stages of aerobic respiration.