Review of Adaptive Immunity definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackReview of Adaptive Immunity definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
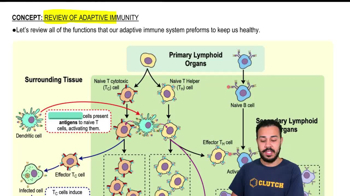
- Adaptive ImmunityA highly specific immune response involving T and B cells, which adapt to recognize and remember specific pathogens.
- Primary Lymphoid OrgansSites where lymphocytes mature; includes the thymus for T cells and bone marrow for B cells.
- Secondary Lymphoid OrgansLocations where mature lymphocytes encounter antigens and become activated, such as lymph nodes and spleen.
- Naive T CellsInactive T cells that have not yet encountered their specific antigen.
- Naive B CellsInactive B cells that have not yet encountered their specific antigen.
- Antigen-Presenting CellsCells like dendritic cells that display antigens on MHC molecules to activate T cells.
- MHC Class IMolecules that present antigens to cytotoxic T cells, typically from intracellular pathogens.
- MHC Class IIMolecules that present antigens to helper T cells, typically from extracellular sources.
- Cytotoxic T CellsEffector T cells that induce apoptosis in infected cells to limit pathogen spread.
- Helper T CellsEffector T cells that activate other immune cells, enhancing their pathogen-fighting abilities.
- Memory CellsLong-lived lymphocytes that provide a faster and stronger response upon re-exposure to the same antigen.
- Plasma CellsDifferentiated B cells that secrete antibodies to tag pathogens for removal.
- AntibodiesProteins secreted by plasma cells that bind to antigens, marking them for elimination.
- CytokinesSignaling molecules released by immune cells to modulate immune responses.
- Dendritic CellsAntigen-presenting cells that activate T cells by presenting antigens on MHC molecules.