Respiration definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackRespiration definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
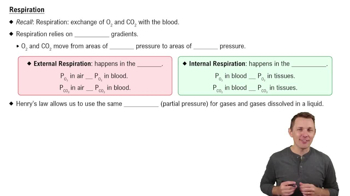
- RespirationThe exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air, blood, and tissues, driven by pressure gradients.
- External RespirationGas exchange between alveolar air and blood, with oxygen moving into blood and carbon dioxide into air.
- Internal RespirationGas exchange between blood and body tissues, with oxygen moving into tissues and carbon dioxide into blood.
- AlveoliTiny air sacs in the lungs where external respiration occurs, facilitating gas exchange with blood.
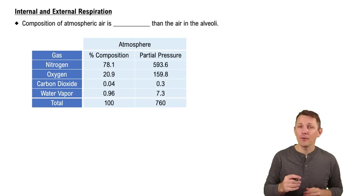
- Partial PressureThe pressure exerted by a single type of gas in a mixture, crucial for understanding gas movement in respiration.
- Henry's LawDescribes the solubility of gases in liquids, explaining why carbon dioxide is more soluble than oxygen.
- HemoglobinA protein in red blood cells that primarily carries oxygen, binding to it for transport in the bloodstream.
- Pressure GradientThe difference in partial pressures that drives the movement of gases during respiration.
- Blood PlasmaThe liquid component of blood where gases like carbon dioxide dissolve and are transported.
- Tidal VolumeThe amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing, typically around 500 milliliters.
- Residual CapacityThe volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal exhalation, preventing lung collapse.
- Intrapulmonary PressureThe pressure within the alveoli, which equalizes with atmospheric pressure during ventilation.
- Cellular RespirationThe metabolic process in tissues using oxygen and producing carbon dioxide as a waste product.
- SolubilityThe ability of a gas to dissolve in a liquid, affecting how gases are transported in the blood.
- Metabolic ActivityThe level of biochemical processes in tissues, influencing the gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide.