Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
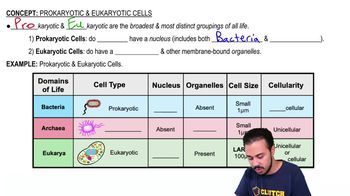
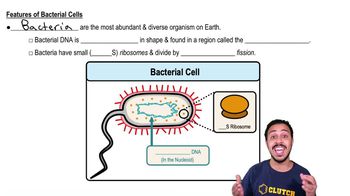
- Prokaryotic cellsCells lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, typically unicellular and smaller in size.
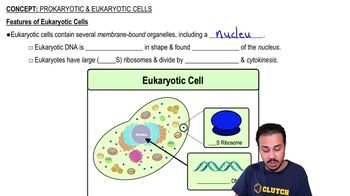
- Eukaryotic cellsCells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, can be unicellular or multicellular, and are larger in size.
- NucleusMembrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells housing linear DNA.
- NucleoidRegion in prokaryotic cells where circular DNA is located.
- RibosomesCell structures responsible for protein synthesis, differing in size between cell types.
- Binary fissionSimple cell division process in prokaryotic cells.
- MitosisComplex cell division process in eukaryotic cells, involving cytokinesis.
- CytokinesisProcess following mitosis, dividing the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
- Circular DNADNA structure found in prokaryotic cells.
- Linear DNADNA structure found in eukaryotic cells.
- Membrane-bound organellesStructures within eukaryotic cells, absent in prokaryotic cells.
- 70S ribosomesSmaller ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells.
- 80S ribosomesLarger ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells.
- Cell membraneStructure surrounding all cells, maintaining the cell's environment.
- BiomoleculesEssential molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids found in all cells.