Primary Lymphoid Organs definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPrimary Lymphoid Organs definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- HematopoiesisThe process of blood cell formation, including the production of T and B lymphocytes in the red bone marrow.
- LymphocytopoiesisThe formation of lymphocytes, specifically T and B cells, originating in the red bone marrow.
- ImmunocompetentThe state of being capable of carrying out an effective immune response against specific pathogens.
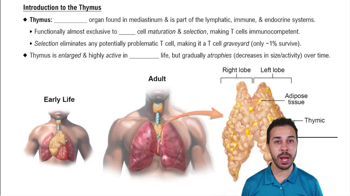
- ThymusA bilobed organ in the mediastinum essential for T cell maturation and selection, part of the lymphatic, immune, and endocrine systems.
- MediastinumThe region in the upper chest behind the sternum, between the lungs, and above the heart, where the thymus is located.
- Blood-thymus barrierA barrier formed by thymic epithelial cells preventing antigens in the blood from disrupting T cell maturation in the thymus.
- TrabeculaeInward capsular extensions of dense irregular connective tissue dividing the thymus lobes into smaller lobules.
- LobulesSmaller compartments within each lobe of the thymus, containing an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
- Outer cortexThe region in thymic lobules where premature T cells begin their maturation process.
- Inner medullaThe region in thymic lobules containing mature T cells, marked by lighter staining in micrographs.
- Thymic corpusclesConcentric whorls of thymic epithelial cells in the inner medulla, involved in regulatory T cell development.
- Regulatory T cellsA special type of T cell developed in the thymus, important for preventing autoimmune diseases.
- Adipose tissueFatty tissue that accumulates in the thymus as it atrophies with age, replacing thymic tissue.
- Thymic epithelial cellsSpecialized cells in the thymus forming the blood-thymus barrier and thymic corpuscles, secreting signaling molecules.
- Thymic atrophyThe process of the thymus decreasing in size and activity over time, with tissue replaced by fibrous and fatty tissue.