Platelets: Hemostasis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPlatelets: Hemostasis definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
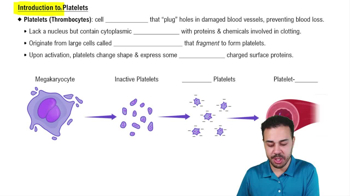
- PlateletsCell fragments crucial for blood clotting, lacking a nucleus but containing granules essential for the clotting process.
- ThrombocytesAnother term for platelets, involved in plugging damaged vessel walls to prevent blood loss.
- HemostasisThe process to prevent and control bleeding, involving vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and coagulation.
- Vascular SpasmImmediate constriction of damaged blood vessels to reduce blood flow and blood loss.
- Platelet PlugAggregation of platelets at a damaged site to form a temporary seal to prevent blood loss.
- CoagulationReinforcement of the platelet plug with fibrin to form a stable blood clot.
- FibrinProtein that acts as molecular glue, stabilizing the platelet plug during coagulation.
- MegakaryocytesLarge cells that fragment to form platelets.
- Von Willebrand FactorPlasma protein that binds to exposed collagen, aiding platelet adhesion at injury sites.
- Prothrombin ActivatorEnzyme that converts prothrombin to thrombin in the coagulation cascade.
- ThrombinEnzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin, crucial for blood clot stabilization.
- FibrinolysisProcess of breaking down fibrin to remove the blood clot after vessel healing.
- PlasminActive enzyme that digests fibrin, aiding in clot removal during fibrinolysis.
- Clot RetractionProcess where the blood clot contracts to stabilize and pull vessel edges together.
- Cytoplasmic GranulesStructures within platelets containing chemicals crucial for the clotting process.