Placentation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPlacentation definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- PlacentaA temporary organ formed from maternal and fetal tissues, facilitating exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between mother and conceptus.
- HCGA hormone produced by the placenta starting around days 10-12 post-conception, detectable by modern pregnancy tests.
- EstrogenA hormone produced by the placenta, with levels fluctuating throughout pregnancy, supporting gestational processes.
- ProgesteroneA hormone produced by the placenta, crucial for maintaining pregnancy and supporting fetal development.
- Placental lactogenA hormone produced by the placenta, involved in regulating maternal metabolism and fetal growth.
- RelaxinA hormone produced by the placenta, aiding in the relaxation of pelvic ligaments and cervix during pregnancy.
- PlacentationThe process of forming the placenta, beginning during implantation and continuing throughout the fetal period.
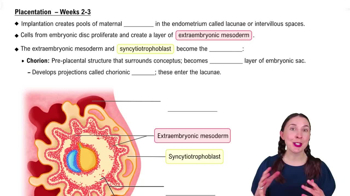
- SyncytiotrophoblastA tissue that releases enzymes to erode the endometrium, forming pools of maternal blood known as lacunae.
- LacunaePools of maternal blood within the endometrium, formed during early placentation for nutrient exchange.
- Extraembryonic mesodermA layer of cells forming around the embryo, contributing to the development of the chorion.
- ChorionA structure formed from extraembryonic mesoderm and syncytiotrophoblast, developing into the outer layer of the embryonic sac.
- Chorionic villiProjections from the chorion that enter lacunae, serving as the main site of exchange between mother and conceptus.
- Umbilical arteriesBlood vessels that connect the chorionic villi to the fetal circulatory system, facilitating nutrient and gas exchange.
- Umbilical veinA blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus, part of the umbilical cord.
- EndometriumThe uterine lining that undergoes changes to support placentation, contributing to the maternal portion of the placenta.