Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
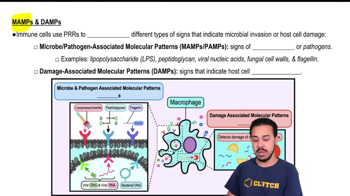
- Pattern Recognition ReceptorsCell surface receptors on immune cells that detect microbial invasion and host cell damage.
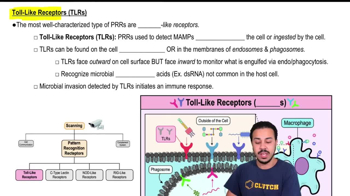
- Toll-like ReceptorsMembrane-embedded receptors that detect MAMPs outside or ingested by the cell.
- C-type Lectin ReceptorsCell surface receptors that bind to carbohydrate MAMPs on microbial surfaces.
- Nod-like ReceptorsCytoplasmic receptors that detect intracellular MAMPs and DAMPs, forming inflammasomes.
- RIG-like ReceptorsCytoplasmic receptors that detect viral RNA, distinguishing it from host RNA.
- MAMPsMicrobe-associated molecular patterns indicating microbial presence.
- DAMPsDamage-associated molecular patterns indicating host cell damage.
- CytokinesSignaling proteins released by cells, especially in response to PRR activation.
- EndosomesMembrane-bound compartments within cells, involved in transporting ingested materials.
- PhagosomesVesicles formed around a particle engulfed by phagocytosis, containing PRRs.
- LipopolysaccharideComponent of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, detected by PRRs.
- PeptidoglycanMolecule specific to bacterial cell walls, recognized by PRRs.
- FlagellinProtein component of bacterial flagella, detected as a MAMP by PRRs.
- InflammasomeProtein complex formed by NLRs that activates pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
- InterferonCytokine released in response to viral infections, often triggered by RIG-like receptors.