Osmosis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackOsmosis definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
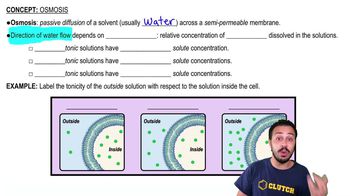
- OsmosisPassive diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane driven by solute concentration differences.
- Semipermeable membraneA barrier that allows certain substances to pass while blocking others, crucial for osmosis.
- SolventA substance, typically water in biology, that dissolves solutes, facilitating osmosis.
- TonicityRelative concentration of solutes in solutions, affecting water movement across membranes.
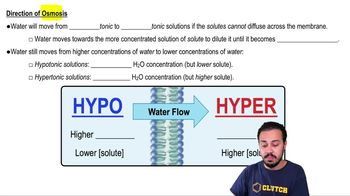
- HypotonicSolution with lower solute concentration, causing water to flow into cells, potentially swelling them.
- IsotonicSolution with equal solute concentration, maintaining cell size as water enters and exits equally.
- HypertonicSolution with higher solute concentration, drawing water out of cells, leading to shrinkage.
- Turgor pressurePressure exerted by water inside the cell against the cell wall, crucial for plant rigidity.
- Cell lysisBursting of a cell due to excessive water intake in hypotonic environments, common in animal cells.
- DehydrationLoss of water from cells in hypertonic environments, causing shrinkage and potential cell death.
- Biological membraneA semipermeable structure surrounding cells, regulating substance passage and facilitating osmosis.
- SoluteSubstance dissolved in a solvent, determining the tonicity of a solution.
- Water concentrationAmount of water in a solution, inversely related to solute concentration in osmosis.
- Cell wallRigid structure in plant cells preventing lysis in hypotonic environments by maintaining shape.
- Environmental tonicityExternal solution's solute concentration affecting cell water movement and behavior.