Organization of the Body: Serous Membrane Locations definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackOrganization of the Body: Serous Membrane Locations definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Serous MembranesThin tissues that line certain internal cavities, reducing friction between organs during movement.
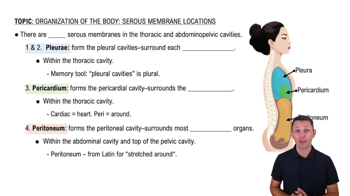
- PleuraeMembranes forming pleural cavities, surrounding each lung, allowing lung movement without friction.
- PericardiumMembrane forming the pericardial cavity, surrounding the heart, facilitating its movement.
- PeritoneumMembrane forming the peritoneal cavity, surrounding most digestive organs, allowing complex organ movement.
- Visceral LayerThe part of a serous membrane that directly contacts and covers an organ.
- Parietal LayerThe part of a serous membrane that lines the body wall or cavity.
- Pleural CavitiesSpaces created by pleurae surrounding each lung, allowing lung expansion and contraction.
- Pericardial CavitySpace formed by the pericardium surrounding the heart, enabling its movement.
- Peritoneal CavityComplex space formed by the peritoneum, surrounding various digestive organs.
- Visceral PericardiumThe layer of the pericardium that directly touches the heart.
- Parietal PleuraThe layer of pleura that lines the chest wall, surrounding the lungs.
- Visceral PeritoneumThe layer of the peritoneum that directly contacts abdominal organs.
- Parietal PeritoneumThe layer of the peritoneum that lines the abdominal wall.
- Thoracic CavityThe body cavity housing the lungs and heart, enclosed by the rib cage.
- Abdominal CavityThe body cavity containing most digestive organs, part of the peritoneal cavity.