Organization of Sensory Pathways definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackOrganization of Sensory Pathways definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Somatosensory SystemPart of the sensory system serving the body wall and limbs, involving general senses like touch and proprioception.
- Special SensesSenses with receptors in complex organs, including vision, hearing, taste, smell, and equilibrium.
- General SensesSenses with simple receptors, including touch, pain, temperature, vibration, pressure, and proprioception.
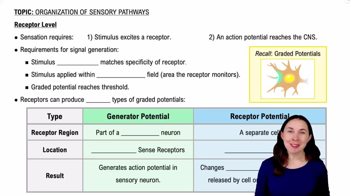
- Receptor LevelThe initial stage of sensory processing where stimuli activate sensory receptors.
- Circuit LevelStage involving ascending pathways that transmit impulses to the brain.
- Perceptual LevelStage where the brain processes and interprets sensory information, leading to conscious awareness.
- Receptive FieldThe area monitored by a sensory receptor, where stimuli must be applied to be detected.
- Graded PotentialA change in membrane potential that must reach threshold to trigger an action potential.
- Generator PotentialA graded potential occurring directly in sensory neurons, common in general sense receptors.
- Receptor PotentialA graded potential involving a separate receptor cell affecting a sensory neuron, common in special senses.
- Ascending PathwaysNeural pathways that carry sensory information from receptors to the brain.
- Afferent NervesNerves that carry sensory signals from receptors toward the central nervous system.
- Somatosensory CortexBrain region where sensory information is processed and interpreted.
- NeurotransmitterChemical released by neurons to transmit signals across a synapse to another neuron.
- Cerebral CortexThe outer layer of the brain involved in processing sensory input and conscious perception.