Nucleic Acids definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackNucleic Acids definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Nucleic AcidsPolymers that store and encode genetic information, composed of nucleotide monomers.
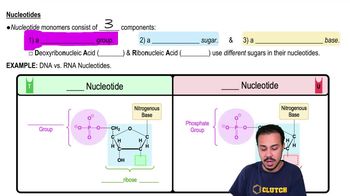
- NucleotidesMonomers of nucleic acids, consisting of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
- Phosphate GroupA functional group in nucleotides, containing a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms.
- Pentose SugarA five-carbon sugar in nucleotides; deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA.
- Nitrogenous BaseA component of nucleotides, categorized as pyrimidines or purines, involved in base pairing.
- Phosphodiester BondCovalent bond linking nucleotides in nucleic acids, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone.
- Sugar-Phosphate BackboneThe structural framework of nucleic acids, consisting of alternating sugar and phosphate groups.
- DirectionalityOrientation of nucleic acid strands, indicated by 5' and 3' ends, affecting polymer structure.
- PyrimidinesSingle-ringed nitrogenous bases, including cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
- PurinesDouble-ringed nitrogenous bases, including adenine and guanine.
- Base PairingHydrogen bonding between complementary nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA.
- Double HelixThe twisted ladder structure of DNA, consisting of two antiparallel strands.
- AntiparallelOrientation of DNA strands running in opposite directions, crucial for double helix structure.
- DeoxyriboseThe sugar in DNA nucleotides, lacking one oxygen atom compared to ribose.
- RiboseThe sugar in RNA nucleotides, containing a hydroxyl group at the 2' position.