Neurotransmitters of the ANS definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackNeurotransmitters of the ANS definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
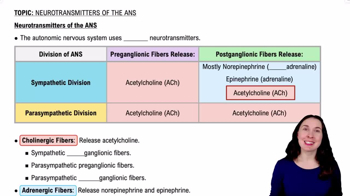
- AcetylcholineA neurotransmitter released by all preganglionic fibers and parasympathetic postganglionic fibers in the ANS.
- NorepinephrineA neurotransmitter primarily released by sympathetic postganglionic fibers, crucial for the fight or flight response.
- EpinephrineAlso known as adrenaline, released by some sympathetic postganglionic fibers and the adrenal medulla.
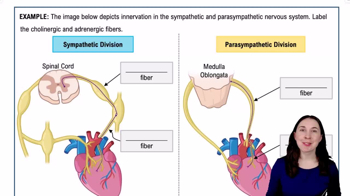
- Cholinergic fibersFibers that release acetylcholine, including all preganglionic fibers and parasympathetic postganglionic fibers.
- Adrenergic fibersFibers that release norepinephrine and epinephrine, primarily found in sympathetic postganglionic fibers.
- Nicotinic receptorsA subtype of cholinergic receptors found at all ANS synapses between pre and postganglionic fibers.
- Muscarinic receptorsCholinergic receptors located at parasympathetic target organs and sympathetic sweat glands.
- Adrenergic receptorsReceptors that bind norepinephrine and epinephrine, found at sympathetic target organs.
- Alpha receptorsA subtype of adrenergic receptors, involved in various sympathetic responses.
- Beta receptorsAnother subtype of adrenergic receptors, playing a role in sympathetic nervous system activities.
- Preganglionic fibersNerve fibers in the ANS that release acetylcholine at synapses with postganglionic fibers.
- Postganglionic fibersNerve fibers that release neurotransmitters at target organs, varying by ANS division.
- Sympathetic divisionPart of the ANS that prepares the body for fight or flight, using norepinephrine and epinephrine.
- Parasympathetic divisionPart of the ANS that conserves energy, using acetylcholine for both pre and postganglionic fibers.
- Adrenal medullaA sympathetic structure in the adrenal gland that releases epinephrine and norepinephrine.