Ions - Sodium and Potassium definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIons - Sodium and Potassium definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
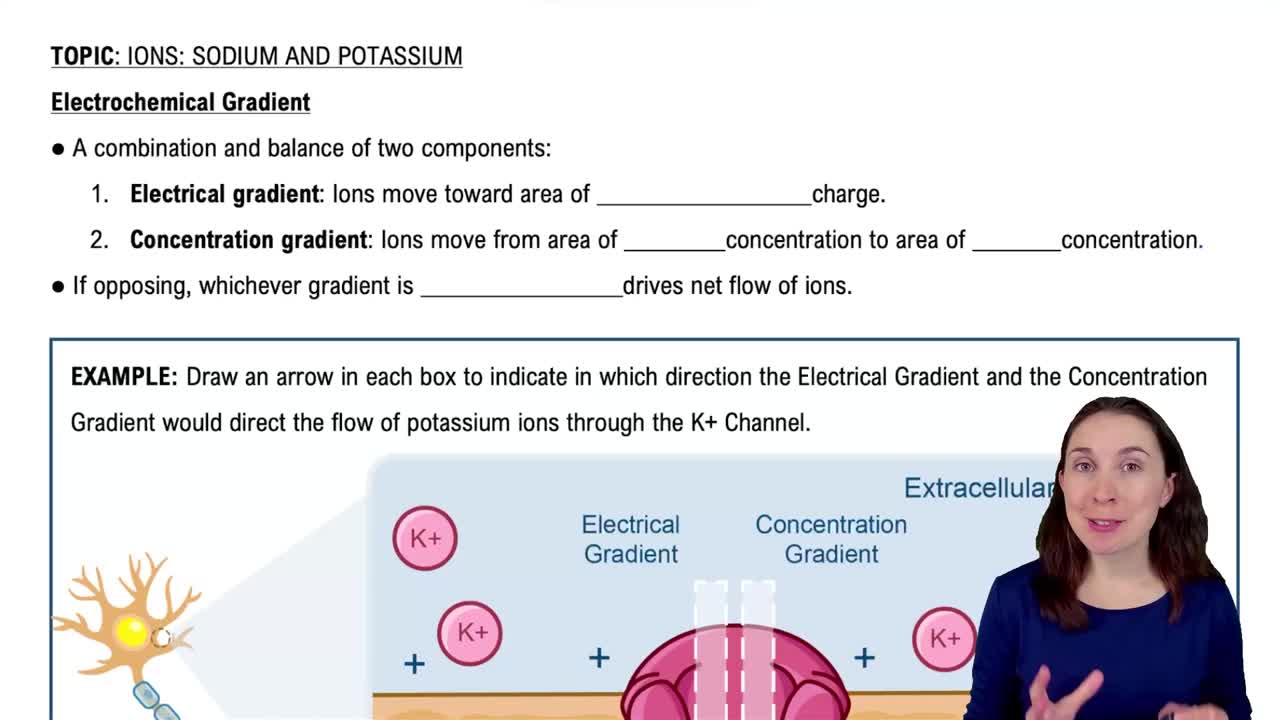
- Electrochemical GradientA force combining electrical and concentration gradients, influencing ion movement across cell membranes.
- Electrical GradientA force causing ions to move toward areas of opposite charge, based on the principle that opposites attract.
- Concentration GradientA force driving ions from high to low concentration areas, influencing the rate of ion diffusion.
- Sodium-Potassium PumpAn ATP-consuming pump that ejects 3 sodium ions and imports 2 potassium ions, moving them against their gradients.
- ATPA molecule providing energy for active transport processes like the sodium-potassium pump.
- NeuronA cell type where sodium and potassium ion concentrations are crucial for resting and active states.
- CytosolThe negatively charged fluid inside a cell where potassium ions are typically more concentrated.
- Extracellular FluidThe positively charged fluid outside a cell where sodium ions are typically more concentrated.
- Leak ChannelA channel allowing ions to move freely across the cell membrane, contributing to resting ion distribution.
- Active TransportA process moving ions against their electrochemical gradients using energy from ATP.
- Resting StateA condition where a neuron is not transmitting signals, with specific ion concentration distributions.
- DiffusionThe passive movement of ions from high to low concentration areas, driven by concentration gradients.
- Potassium IonA positively charged ion with higher intracellular concentration, moving via concentration and electrical gradients.
- Sodium IonA positively charged ion with higher extracellular concentration, moving via concentration and electrical gradients.
- Chemical GradientAnother term for concentration gradient, emphasizing ion movement from high to low concentration areas.