Introduction to the Integumentary System definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to the Integumentary System definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
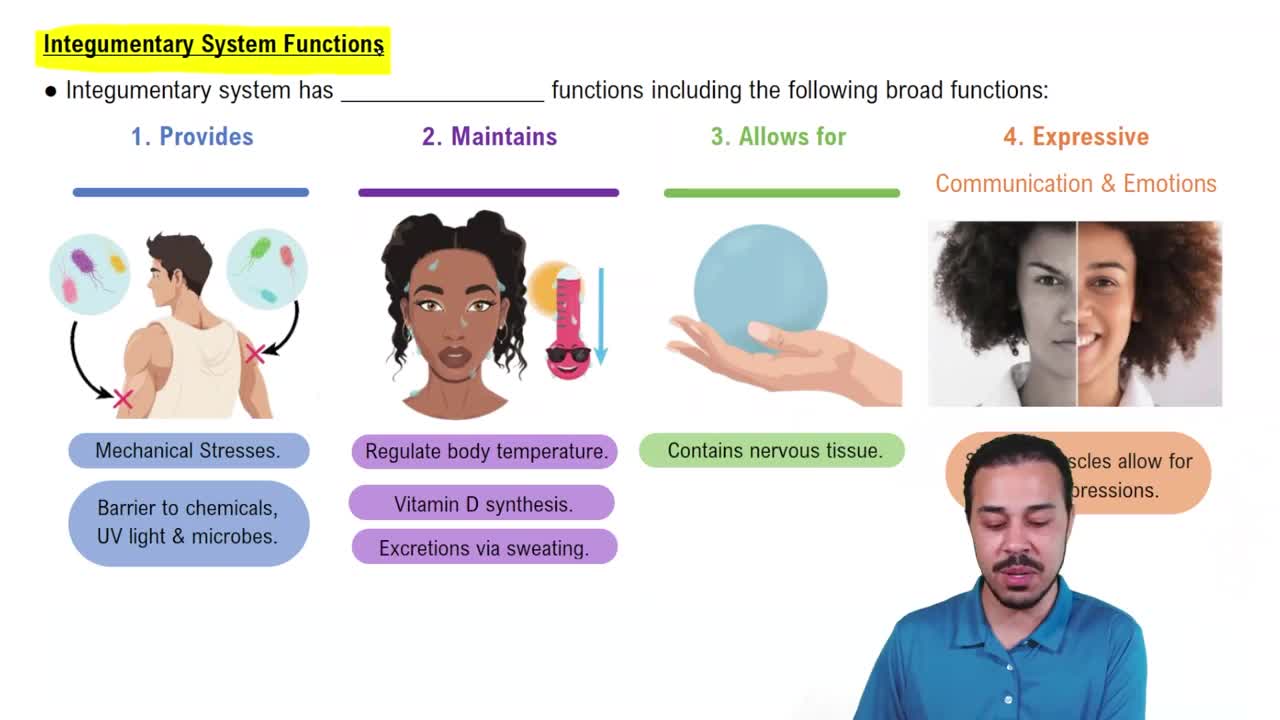
- Integumentary SystemComprises skin, hair, nails, glands, and sensory receptors, providing protection, sensation, and homeostasis.
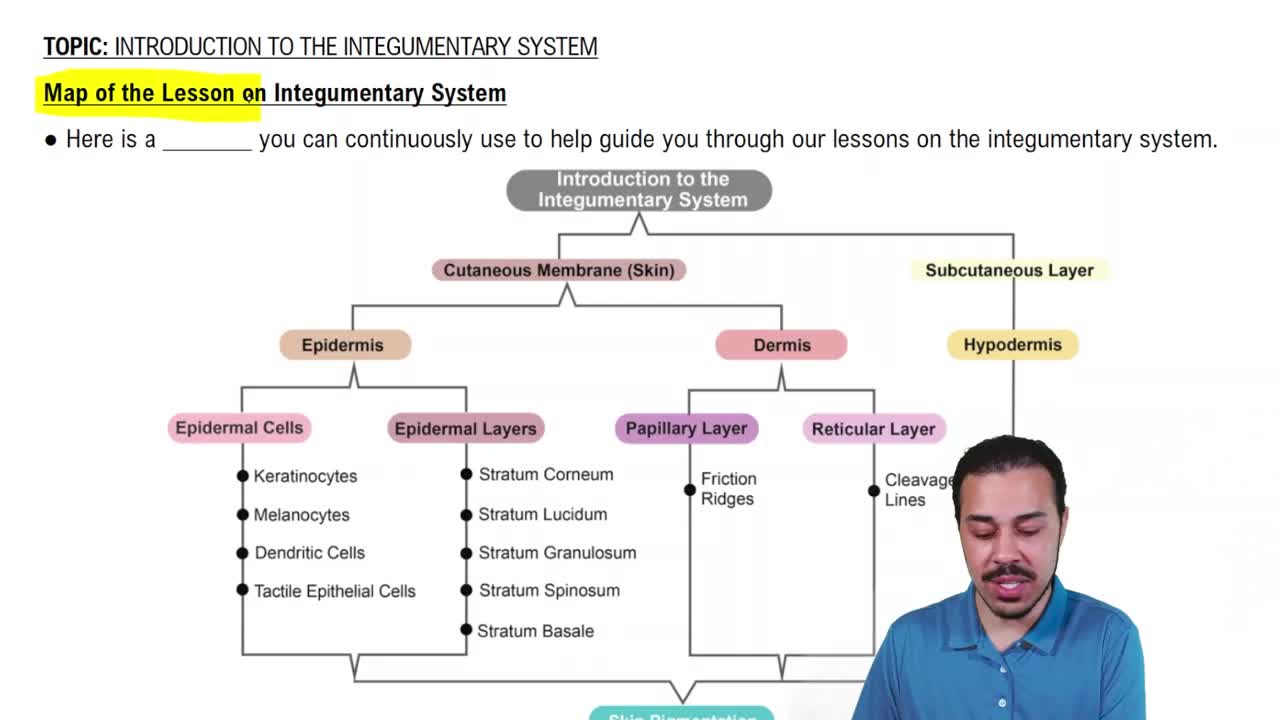
- EpidermisOutermost skin layer made of stratified squamous epithelial tissue, providing a barrier to the external environment.
- DermisLayer beneath the epidermis, composed mainly of connective tissue, housing blood vessels, nerves, and glands.
- HypodermisSubcutaneous layer beneath the skin, consisting of fat and connective tissue, providing insulation and cushioning.
- Cutaneous MembraneAnother term for skin, consisting of the epidermis and dermis, serving as a protective barrier.
- Accessory StructuresIncludes hair, nails, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands, contributing to the skin's functions.
- Stratified Squamous EpitheliumType of epithelial tissue in the epidermis, consisting of multiple layers of flat cells.
- HomeostasisProcess of maintaining stable internal conditions despite external changes, aided by the integumentary system.
- KeratinocytesCells in the epidermis responsible for producing keratin, a protein that strengthens the skin.
- MelanocytesCells in the epidermis that produce melanin, contributing to skin pigmentation and UV protection.
- Sebaceous GlandsOil-producing glands in the skin, helping to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair.
- Sweat GlandsGlands in the skin responsible for producing sweat, aiding in temperature regulation and waste excretion.
- Sensory ReceptorsNerve endings in the skin that detect sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain.
- Vitamin D SynthesisProcess initiated in the skin under UV light, crucial for bone health and calcium regulation.
- Nonverbal CommunicationExpression of emotions through facial expressions, facilitated by the skin and underlying muscles.