Introduction to T Lymphocytes definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to T Lymphocytes definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
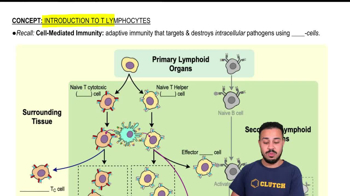
- T LymphocytesCrucial cells in adaptive immunity, targeting intracellular pathogens through cell-mediated responses.
- ThymusPrimary lymphoid organ where T cells develop before migrating to secondary lymphoid organs.
- Cytotoxic T CellsT cells responsible for inducing apoptosis in cells infected with intracellular pathogens.
- Helper T CellsT cells that aid in activating other immune cells by producing cytokines.
- Antigen-Presenting CellsCells like dendritic cells that present antigens to T cells for activation.
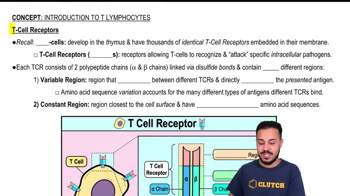
- T Cell Receptors (TCRs)Receptors on T cells that recognize specific antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells.
- Alpha and Beta ChainsPolypeptide chains in TCRs linked by disulfide bonds, crucial for antigen recognition.
- Variable RegionPart of TCRs that varies between different receptors and binds to specific antigens.
- Constant RegionPart of TCRs that remains relatively unchanged and is located near the cell surface.
- Naive T CellsInactive T cells that have not yet encountered their specific antigen.
- Effector T CellsShort-lived T cells that respond immediately to infections upon activation.
- Memory T CellsLong-lived T cells that provide a rapid response to subsequent exposures to the same antigen.
- CD8Protein marker on cytotoxic T cells used to identify and dictate their function.
- CD4Protein marker on helper T cells used to identify and dictate their function.
- CytokinesSignaling proteins produced by helper T cells to activate other immune cells.