Introduction to Organ Systems definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Organ Systems definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Integumentary SystemComprises the skin, hair, and nails, providing protection, a waterproof barrier, and thermal regulation.
- Skeletal SystemConsists of bones and cartilage, providing structure, shape, and protection to the body.
- Muscular SystemEnables movement through muscle contraction, working closely with the skeletal system.
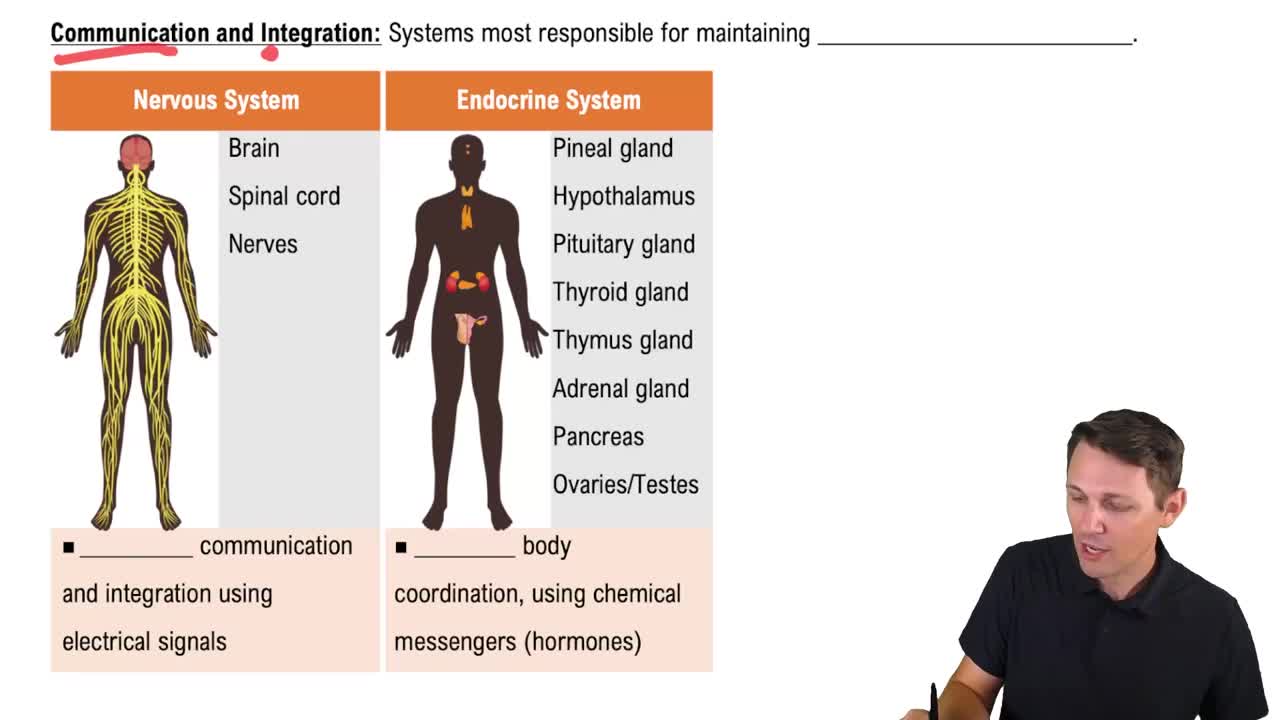
- Nervous SystemIncludes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, facilitating rapid communication and integration via electrical signals.
- Endocrine SystemComposed of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream for whole-body communication and regulation.
- Circulatory SystemComprises the heart, blood vessels, and blood, transporting materials like oxygen, nutrients, and waste throughout the body.
- Lymphatic SystemIncludes lymphatic vessels and nodes, transporting water and aiding the immune system in fighting infections.
- Respiratory SystemConsists of the lungs and airways, facilitating gas exchange, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the environment.
- Digestive SystemInvolves the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and accessory organs, breaking down food and absorbing nutrients and water.
- Urinary SystemIncludes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, removing waste and excess water from the blood.
- Reproductive SystemInvolves organs like the testes and ovaries, responsible for producing gametes and supporting reproduction.
- HomeostasisThe maintenance of a stable internal environment within the body, primarily regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems.
- HormonesChemical messengers produced by endocrine glands, traveling through the bloodstream to regulate various body functions.
- Immune SystemA network of cells and tissues that work together to defend the body against infections and diseases.
- CartilageA flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the body, providing support and cushioning in joints.