Introduction to Muscles and Muscle Tissue definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Muscles and Muscle Tissue definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
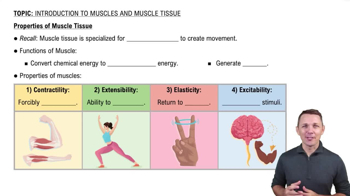
- ContractilityThe ability of muscle tissue to shorten forcibly, generating movement.
- ExtensibilityThe capacity of muscle tissue to be stretched without damage.
- ElasticityThe property of muscle tissue to return to its original shape after contraction or extension.
- ExcitabilityThe ability of muscle tissue to respond to stimuli, often through action potentials.
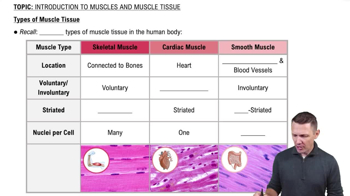
- Skeletal MuscleVoluntary, striated muscle tissue attached to bones, responsible for body movement.
- Cardiac MuscleInvoluntary, striated muscle found in the heart, characterized by a branching pattern.
- Smooth MuscleInvoluntary, non-striated muscle found in hollow organs, controlling movement within them.
- StriationsCrosswise stripes in muscle tissue indicating organized protein structures.
- Intercalated DiscsStructures in cardiac muscle linking cells, facilitating synchronized contraction.
- ATPThe primary energy carrier in cells, used by muscles to convert chemical energy into movement.
- NucleiCellular structures containing genetic material; skeletal muscle cells have multiple due to their size.
- Voluntary MuscleMuscle that can be consciously controlled, such as skeletal muscle.
- Involuntary MuscleMuscle that operates without conscious control, like cardiac and smooth muscle.
- Mechanical EnergyEnergy associated with the movement and position of an object, produced by muscle contraction.
- HomeostasisThe body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions, aided by muscle-generated heat.