Introduction to Inflammation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Inflammation definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- InflammationA coordinated immune response to infection or tissue damage, marked by swelling, heat, altered function, redness, and pain.
- SHARPAn acronym for the five cardinal signs of inflammation: Swelling, Heat, Altered function, Redness, and Pain.
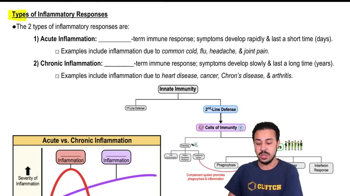
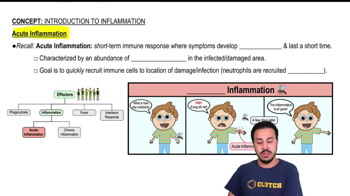
- Acute inflammationA short-term immune response characterized by rapid symptom development and an abundance of neutrophils.
- Chronic inflammationA long-term immune response with slow symptom development, involving macrophages, giant cells, and T lymphocytes.
- NeutrophilsImmune cells that are the first to arrive at the site of infection during acute inflammation.
- MacrophagesImmune cells involved in chronic inflammation, capable of forming giant cells and granulomas.
- Giant cellsFormed by the fusion of two macrophages, these cells are involved in chronic inflammation.
- T lymphocytesCells of the adaptive immune system that play a role in chronic inflammation and granuloma formation.
- GranulomaA structure formed by immune cells to wall off microbes that cannot be easily destroyed during chronic inflammation.
- Innate immunityThe body's second line of defense, involving non-specific responses like inflammation.
- Rheumatoid arthritisAn example of chronic inflammation where the immune system causes long-term joint inflammation.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosisThe bacterium that causes tuberculosis, often associated with granuloma formation in chronic inflammation.
- PhagocytosisThe process by which cells, like neutrophils, engulf and digest pathogens and debris.
- Adaptive immunityThe immune system's ability to recognize and remember specific pathogens for more efficient responses.
- Tissue repairThe process of healing and restoring tissue function following damage or infection.