Introduction to Cellular Respiration definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Cellular Respiration definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
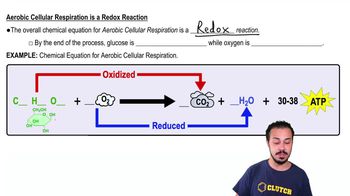
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationA process that breaks down glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, primarily occurring in the mitochondria.
- ATPThe main energy source for cells, produced in large amounts during aerobic cellular respiration.
- MitochondriaThe organelle where most stages of aerobic cellular respiration occur, producing ATP.
- GlucoseA monosaccharide sugar that is oxidized during aerobic cellular respiration to produce ATP.
- OxygenThe final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration, reduced to form water.
- Redox ReactionA chemical reaction involving the transfer of electrons, as seen in aerobic cellular respiration.
- GlycolysisThe first stage of aerobic cellular respiration, occurring in the cytoplasm, breaking down glucose.
- Pyruvate OxidationThe second stage of aerobic cellular respiration, converting pyruvate into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria.
- Krebs CycleAlso known as the citric acid cycle, it's the third stage of aerobic cellular respiration, producing electron carriers.
- Electron Transport ChainThe fourth stage of aerobic cellular respiration, where electrons are transferred to produce ATP.
- ChemiosmosisA process in the electron transport chain where ATP is synthesized using a proton gradient.
- Substrate Level PhosphorylationA method of ATP production during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
- Oxidative PhosphorylationATP production method in the electron transport chain using oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
- FermentationAn anaerobic process that allows glycolysis to continue by regenerating NAD+, producing lactic acid or alcohol.
- Carbon DioxideA byproduct of aerobic cellular respiration, produced when glucose is oxidized.