Introduction to B Lymphocytes definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to B Lymphocytes definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
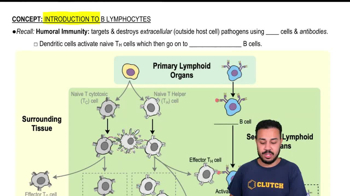
- B lymphocytesCells crucial for adaptive humoral immunity, targeting extracellular pathogens using antibodies.
- Humoral immunityPart of the adaptive immune system targeting extracellular pathogens with B cells and antibodies.
- AntibodiesProteins secreted by plasma cells that bind to antigens to neutralize or destroy pathogens.
- Bone marrowPrimary lymphoid organ where B cells develop and mature before migrating to secondary organs.
- B cell receptorsMembrane-embedded receptors on B cells that bind free-floating antigens, also known as BCRs.
- AntigenA substance that is recognized by the immune system and can provoke an immune response.
- MHC class II moleculesMolecules on antigen-presenting cells that display processed antigens to helper T cells.
- Helper T cellsCells that assist in activating B cells by recognizing antigens presented on MHC class II molecules.
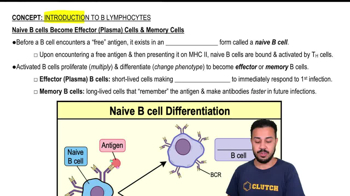
- Plasma cellsEffector B cells that secrete large quantities of antibodies to combat immediate threats.
- Memory B cellsLong-lived cells that respond faster to future infections by remembering the antigen.
- CytokinesSignaling proteins released by cells, such as helper T cells, to activate immune responses.
- EpitopeSpecific part of an antigen that is recognized and bound by an antibody or BCR.
- Naive B cellsInactive B cells that have not yet encountered their specific antigen.
- ClonesIdentical cells produced from a single B cell after activation and proliferation.
- Effector cellsActivated cells that perform a specific immune function, such as plasma cells producing antibodies.