Gross Anatomy of Bones - Structure of a Long Bone definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackGross Anatomy of Bones - Structure of a Long Bone definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- EpiphysisThe wider end of a long bone, consisting of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone, covered with articular cartilage at joints.
- DiaphysisThe tubular shaft of a long bone, primarily composed of compact bone, containing the medullary cavity filled with yellow marrow in adults.
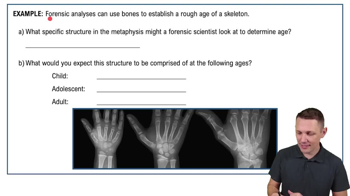
- MetaphysisThe region where the diaphysis and epiphysis meet, housing the epiphyseal plate for bone growth.
- Articular CartilageA smooth, soft layer covering the epiphysis at joints, facilitating easy movement and reducing friction.
- Spongy BoneA porous type of bone found inside the epiphysis, providing structural support and housing marrow.
- Compact BoneDense bone tissue forming the outer layer of bones, providing strength and protection.
- Medullary CavityThe central cavity within the diaphysis of a long bone, containing yellow marrow in adults.
- Yellow MarrowFatty tissue found in the medullary cavity of adult long bones, involved in energy storage.
- Epiphyseal PlateA line of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis, crucial for bone lengthening during growth periods.
- Epiphyseal LineThe remnant of the epiphyseal plate in adults, indicating the end of bone growth in length.
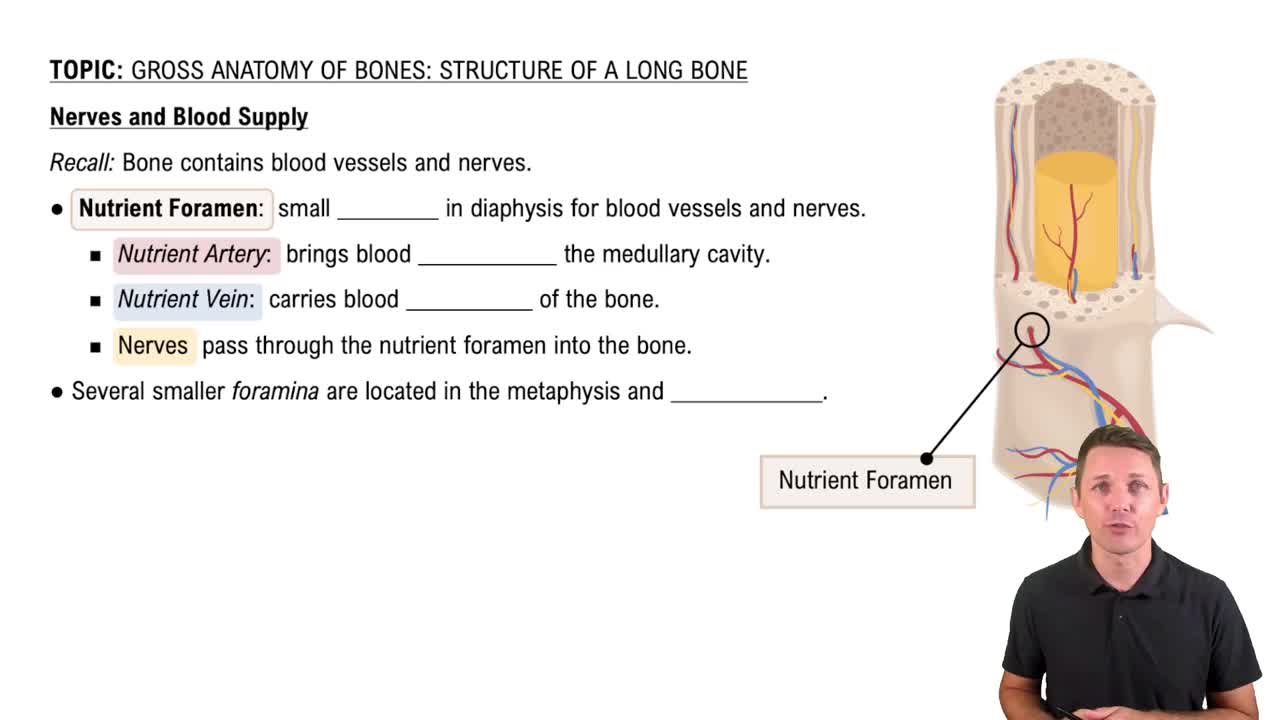
- Nutrient ForamenA macroscopic hole in the diaphysis allowing blood vessels and nerves to enter the bone.
- Nutrient ArteryThe blood vessel that enters through the nutrient foramen to supply the bone and marrow.
- Nutrient VeinThe blood vessel that exits through the nutrient foramen, carrying blood away from the bone.
- ForaminaMultiple small holes in the metaphysis and epiphysis allowing entry of blood vessels and nerves.
- Hyaline CartilageA type of cartilage found in the epiphyseal plate, facilitating bone growth and joint movement.