Gross Anatomy of Bone: Periosteum and Endosteum definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackGross Anatomy of Bone: Periosteum and Endosteum definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
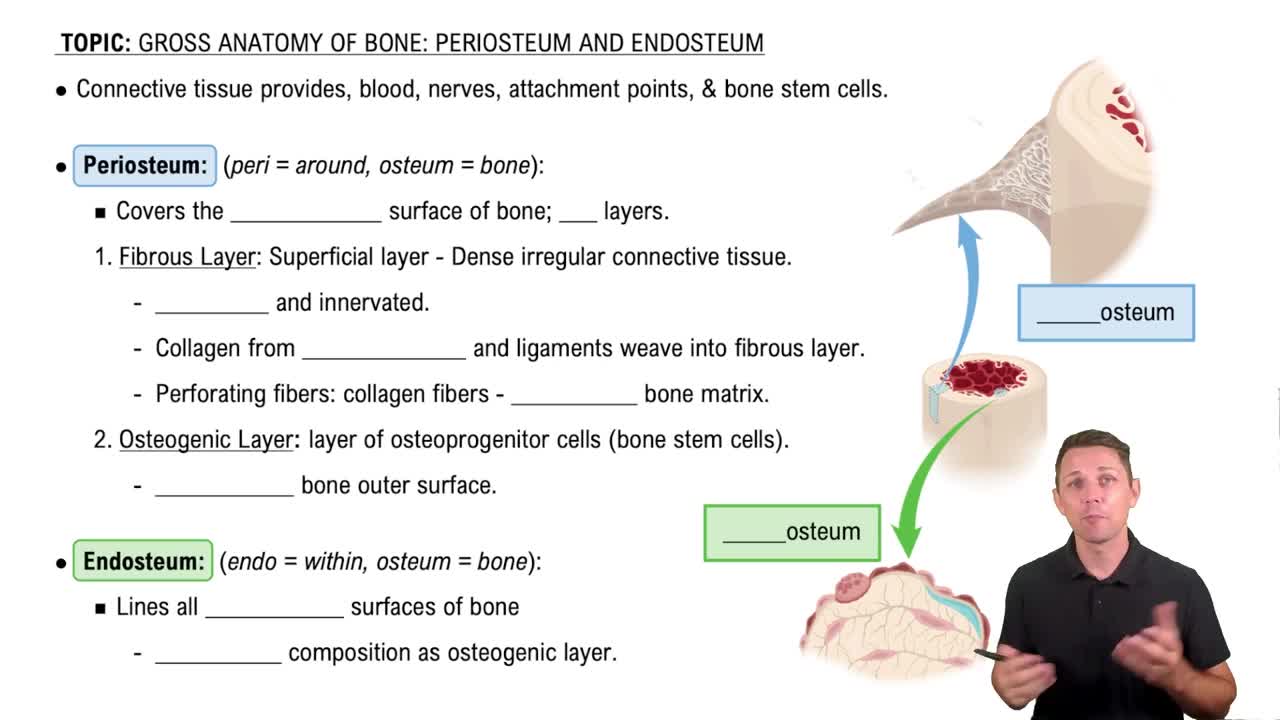
- PeriosteumA dense connective tissue covering the outer surface of bones, providing blood supply, nerves, and attachment points for tendons and ligaments.
- EndosteumA thin membrane lining the inner surfaces of bones, consisting mainly of osteoprogenitor cells for bone remodeling.
- Dense Irregular Connective TissueTissue composed mostly of collagen fibers running in various directions, providing strength and flexibility.
- Osteoprogenitor CellsBone stem cells found in the periosteum and endosteum, essential for bone growth and repair.
- Perforating FibersCollagen fibers that anchor the periosteum to the bone matrix, ensuring a tight connection.
- Fibrous LayerThe outer layer of the periosteum, rich in collagen, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Osteogenic LayerThe inner layer of the periosteum containing osteoprogenitor cells, crucial for bone cell development.
- Compact BoneDense bone tissue forming the outer layer of bones, providing strength and protection.
- Spongy BoneBone tissue with a porous structure, found at the ends of long bones and within the interior of others.
- Medullary CavityThe central cavity of bone shafts where marrow is stored, lined by the endosteum.
- CollagenA strong, rope-like protein that forms the structural framework of connective tissues.
- TendonsConnective tissues that attach muscles to bones, facilitating movement.
- LigamentsConnective tissues that connect bones to other bones, stabilizing joints.
- Bone MatrixThe intercellular substance of bone tissue, consisting of collagen fibers and mineral deposits.
- TrabeculaeThe small, beam-like structures in spongy bone that provide structural support and house bone marrow.