Gluconeogenesis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackGluconeogenesis definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- GluconeogenesisA metabolic pathway that generates glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates, primarily occurring in the liver.
- GlycolysisA process that breaks down glucose into pyruvate, yielding energy in the form of ATP and NADH.
- PyruvateAn end product of glycolysis that can be used in gluconeogenesis or further metabolized in cellular respiration.
- ATPA molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, required in gluconeogenesis to synthesize glucose.
- GTPA nucleotide similar to ATP, used as an energy source in gluconeogenesis to convert oxaloacetate to PEP.
- NADHA coenzyme that carries electrons, used in gluconeogenesis to help convert pyruvate to glucose.
- CytosolThe liquid found inside cells where glycolysis and gluconeogenesis occur.
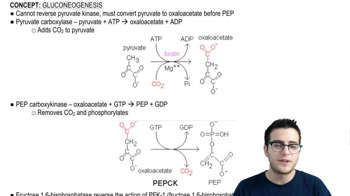
- Pyruvate CarboxylaseAn enzyme that converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate in gluconeogenesis, requiring ATP.
- PEP CarboxykinaseAn enzyme that converts oxaloacetate to PEP in gluconeogenesis, using GTP.
- Fructose 1,6-bisphosphataseAn enzyme that converts fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate in gluconeogenesis.
- Glucose 6-phosphataseAn enzyme found in the liver that converts glucose 6-phosphate to glucose in gluconeogenesis.
- OxaloacetateAn intermediate in gluconeogenesis and the citric acid cycle, formed from pyruvate.
- Futile CycleA situation where two metabolic pathways run simultaneously without net gain, wasting energy.
- LactateA product of anaerobic glycolysis that can be converted back to pyruvate for gluconeogenesis.
- LiverAn organ that plays a crucial role in gluconeogenesis, maintaining blood glucose levels.