Fatty Acid Oxidation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackFatty Acid Oxidation definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
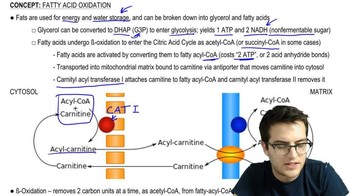
- Beta OxidationA metabolic process in the mitochondrial matrix that breaks down fatty acids into Acetyl CoA, generating ATP.
- Acetyl CoAA molecule that enters the citric acid cycle, produced from fatty acids during beta oxidation.
- Fatty Acyl CoAAn activated form of fatty acids, necessary for transport into mitochondria for beta oxidation.
- Carnitine ShuttleA transport mechanism that moves fatty acyl CoA into the mitochondrial matrix for beta oxidation.
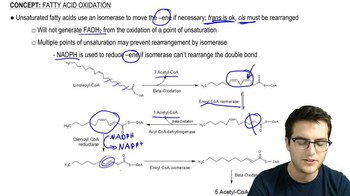
- OxidationThe first step in beta oxidation, converting an -ane to an -ene, reducing FAD to FADH2.
- HydrationThe second step in beta oxidation, adding water to form an alcohol from an -ene.
- ThiolysisThe final step in beta oxidation, cleaving Acetyl CoA from fatty acyl CoA.
- IsomerizationA process required for unsaturated fatty acids to rearrange double bonds for beta oxidation.
- Propanoyl CoAA three-carbon molecule from odd-chain fatty acids, converted to succinyl CoA for the citric acid cycle.
- Succinyl CoAA citric acid cycle intermediate, derived from propanoyl CoA in odd-chain fatty acid oxidation.
- FADH2An electron carrier produced during beta oxidation, contributing to ATP generation.
- NADHAn electron carrier generated in beta oxidation, used in the electron transport chain for ATP production.
- Enoyl CoA HydrataseAn enzyme that hydrates an -ene to form an alcohol during beta oxidation.
- Beta Hydroxy Acyl CoA DehydrogenaseAn enzyme that oxidizes an alcohol to a carbonyl, producing NADH in beta oxidation.
- ThiolaseAn enzyme that cleaves Acetyl CoA from fatty acyl CoA in the final step of beta oxidation.