Endosymbiotic Theory definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEndosymbiotic Theory definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
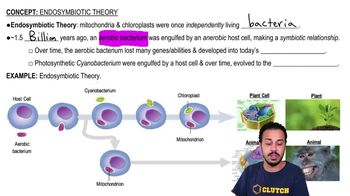
- Endosymbiotic TheoryA theory suggesting mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent bacteria engulfed by host cells.
- MitochondriaOrganelles in eukaryotic cells that evolved from aerobic bacteria engulfed by host cells.
- ChloroplastsOrganelles in plant cells that evolved from photosynthetic cyanobacteria engulfed by host cells.
- Aerobic BacteriumBacteria that use oxygen in metabolism, believed to be the ancestors of mitochondria.
- Anaerobic Host CellCells that do not use oxygen in metabolism, which engulfed aerobic bacteria.
- CyanobacteriumPhotosynthetic bacteria believed to be the ancestors of chloroplasts.
- Symbiotic RelationshipA mutually beneficial relationship between two different organisms.
- ProkaryotesSingle-celled organisms without a nucleus, similar to mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- Circular DNADNA structure found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and prokaryotes.
- 70S RibosomesType of ribosome found in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and prokaryotes.
- Binary FissionA method of replication used by mitochondria, chloroplasts, and prokaryotes.
- Outer MembraneThe external membrane of mitochondria and chloroplasts, consistent with engulfment.
- Inner MembraneThe internal membrane of mitochondria and chloroplasts, consistent with engulfment.
- EngulfmentThe process by which a host cell engulfs another cell, leading to a symbiotic relationship.
- Plant CellsCells containing both mitochondria and chloroplasts, allowing for complex life forms.