Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue definitions Flashcards
 Back
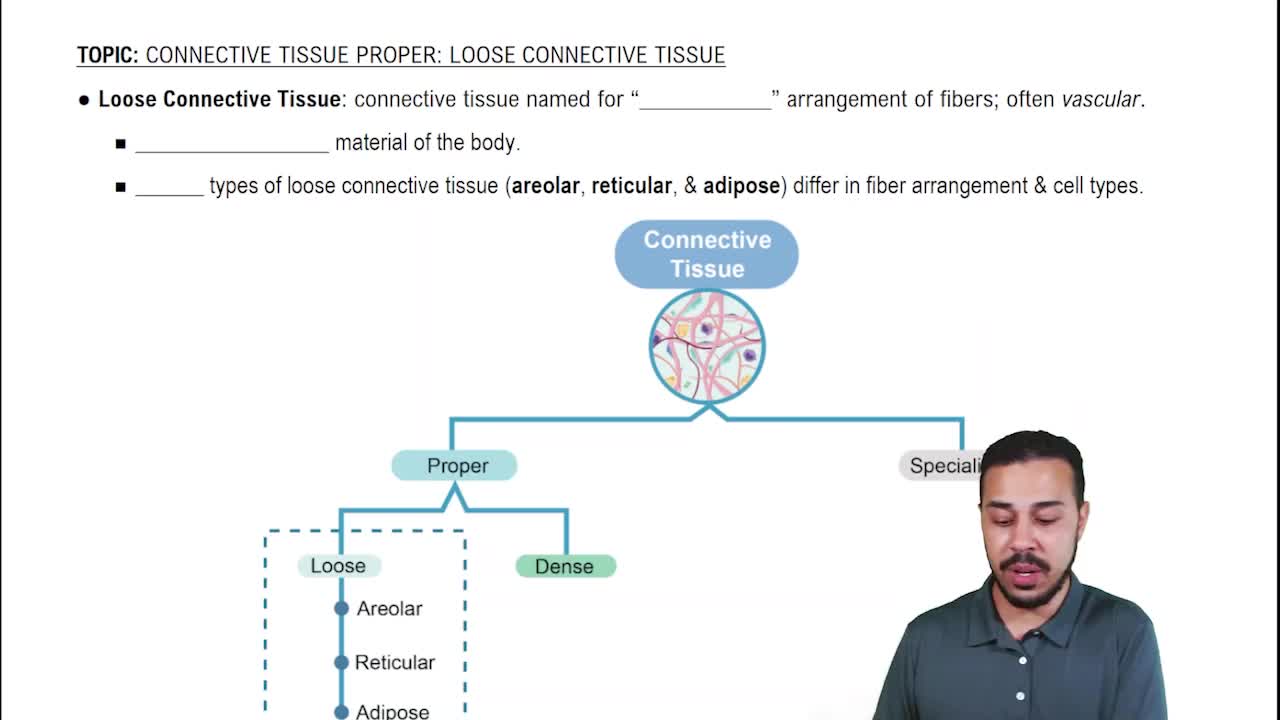
BackConnective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Areolar Connective TissueA type of loose connective tissue with loosely arranged fibers, serving as the body's universal packing material.
- Reticular Connective TissueContains reticular fibers forming a net-like structure, providing internal scaffolding for soft organs.
- Adipose Connective TissueComposed mainly of adipocytes, stores fats, provides insulation, and cushions organs.
- Extracellular MatrixA network of protein fibers and ground substance surrounding cells in connective tissue.
- Collagen FibersStrong, flexible protein fibers found in connective tissues, providing structural support.
- Reticular FibersThin, branching fibers forming a supportive network in reticular connective tissue.
- Elastic FibersFlexible fibers in connective tissue that allow tissues to return to their original shape.
- FibroblastsCells in connective tissue that produce and maintain the extracellular matrix.
- FibrocytesLess active cells in connective tissue responsible for maintaining the extracellular matrix.
- AdipocytesFat cells in adipose tissue that store energy in the form of lipids.
- Mast CellsImmune cells in connective tissue that release histamine, playing a role in inflammation.
- MacrophagesImmune cells in connective tissue that engulf and digest pathogens and debris.
- Ground SubstanceGel-like material in the extracellular matrix that supports cells and fibers.
- White Adipose TissueCommon in adults, stores energy and provides insulation, appearing white under a microscope.
- Brown Adipose TissueRich in mitochondria, found in infants, generates heat to maintain body temperature.