Concentration Gradients and Diffusion definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackConcentration Gradients and Diffusion definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Concentration GradientA difference in the concentration of a substance between two areas, leading to potential movement of molecules.
- EquilibriumA state where the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space, with no net movement.
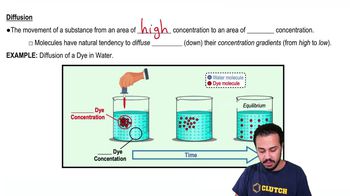
- DiffusionThe net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- EnergyRequired for molecules to move against their concentration gradient, from low to high concentration.
- MoleculeA group of atoms bonded together, which can move along concentration gradients.
- High ConcentrationAn area where a large number of molecules of a substance are present.
- Low ConcentrationAn area where a small number of molecules of a substance are present.
- Net MovementThe overall movement of molecules from one area to another, often from high to low concentration.
- Natural TendencyThe inherent inclination of molecules to move down their concentration gradient.
- BeakerA container used in laboratories, often for mixing or observing chemical reactions.
- DyeA colored substance used to illustrate diffusion in experiments, spreading from high to low concentration.
- Water MoleculeA molecule consisting of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, often used as a solvent.
- AreaA specific region or space where concentration levels can be measured and compared.
- BikerA metaphor used to illustrate the energy dynamics of moving with or against a concentration gradient.
- ImageA visual representation used to explain concepts like concentration gradients and diffusion.