Chemiosmosis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackChemiosmosis definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
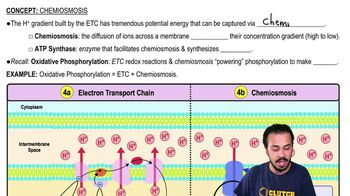
- ChemiosmosisDiffusion of ions across a semipermeable membrane, driven by a concentration gradient created by the electron transport chain.
- Electron Transport ChainSeries of redox reactions that build a hydrogen ion concentration gradient, ultimately powering ATP synthesis.
- Hydrogen Ion Concentration GradientPotential energy source created by the electron transport chain, with high concentration in the intermembrane space.
- ATP SynthaseEnzyme that facilitates chemiosmosis and synthesizes ATP by utilizing the hydrogen ion concentration gradient.
- Oxidative PhosphorylationProcess combining electron transport chain and chemiosmosis to produce ATP in aerobic respiration.
- NADHElectron carrier that donates electrons to the electron transport chain, aiding in ATP production.
- FADH2Electron carrier that transfers electrons to the electron transport chain, contributing to ATP synthesis.
- Intermembrane SpaceArea where hydrogen ions accumulate, creating a concentration gradient for ATP production.
- Mitochondrial MatrixRegion of lower hydrogen ion concentration, where ATP synthase facilitates ATP production.
- Redox ReactionsChemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons, crucial for the electron transport chain.
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationProcess of producing ATP using oxygen, involving oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis.
- PhosphorylationAddition of a phosphate group to ADP, forming ATP, powered by the hydrogen ion gradient.
- Oxygen GasFinal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, reacting to form water.
- Potential EnergyStored energy in the hydrogen ion concentration gradient, used to power ATP synthesis.
- Semipermeable MembraneBarrier allowing selective passage of ions, crucial for maintaining concentration gradients.