Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCharacteristics of Epithelial Tissue definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
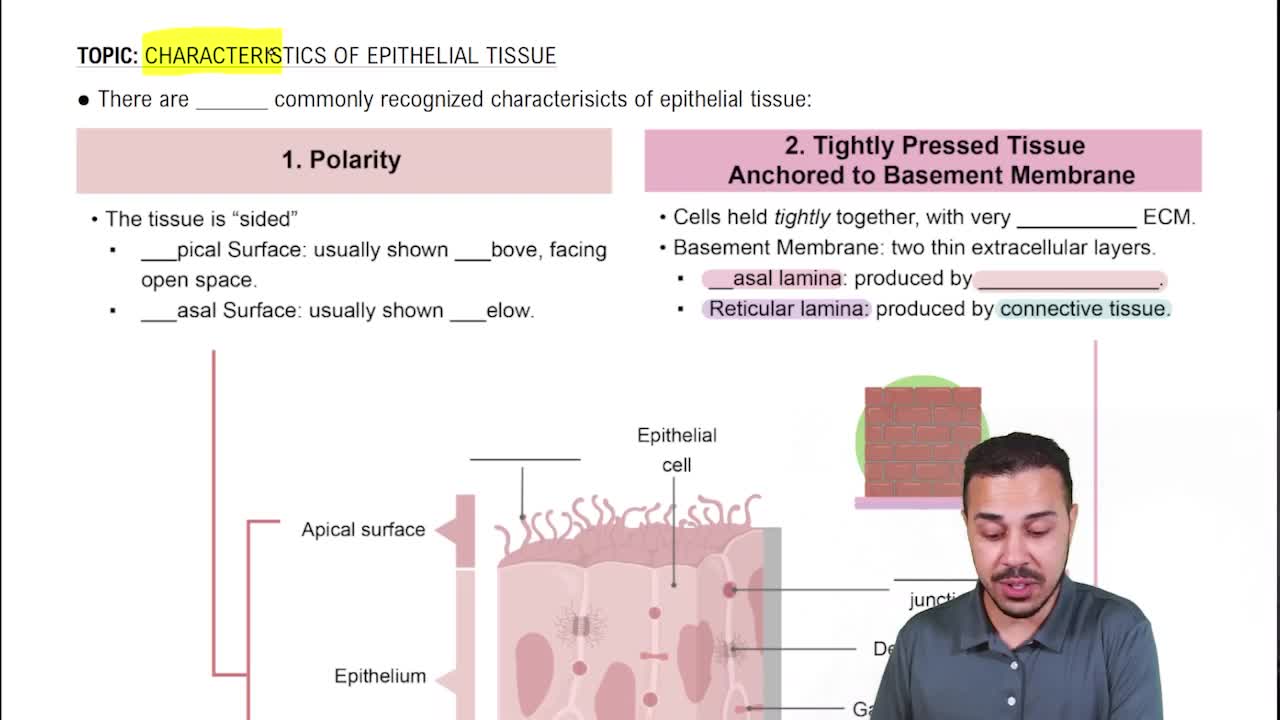
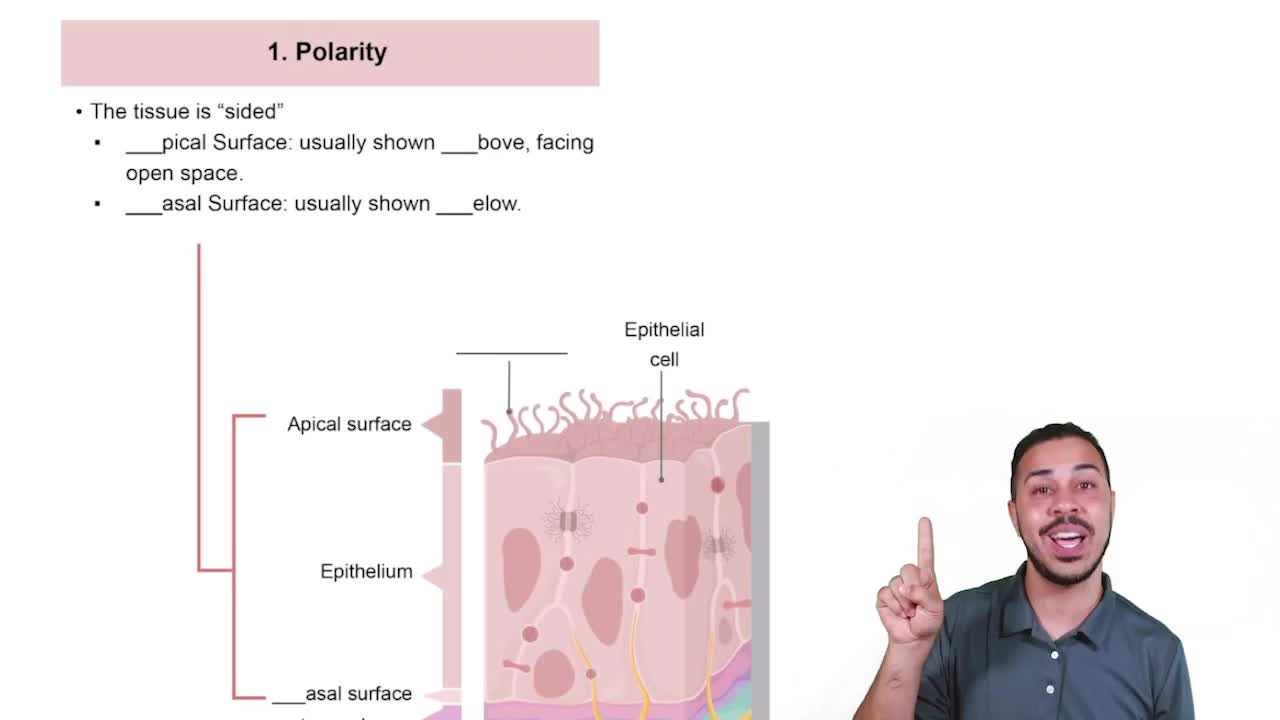
- PolarityDistinct apical and basal surfaces in epithelial tissue, each with unique structures and functions.
- Apical SurfaceThe surface of epithelial tissue facing open space, often containing cilia or microvilli.
- Basal SurfaceThe surface of epithelial tissue facing the basement membrane, anchoring the tissue.
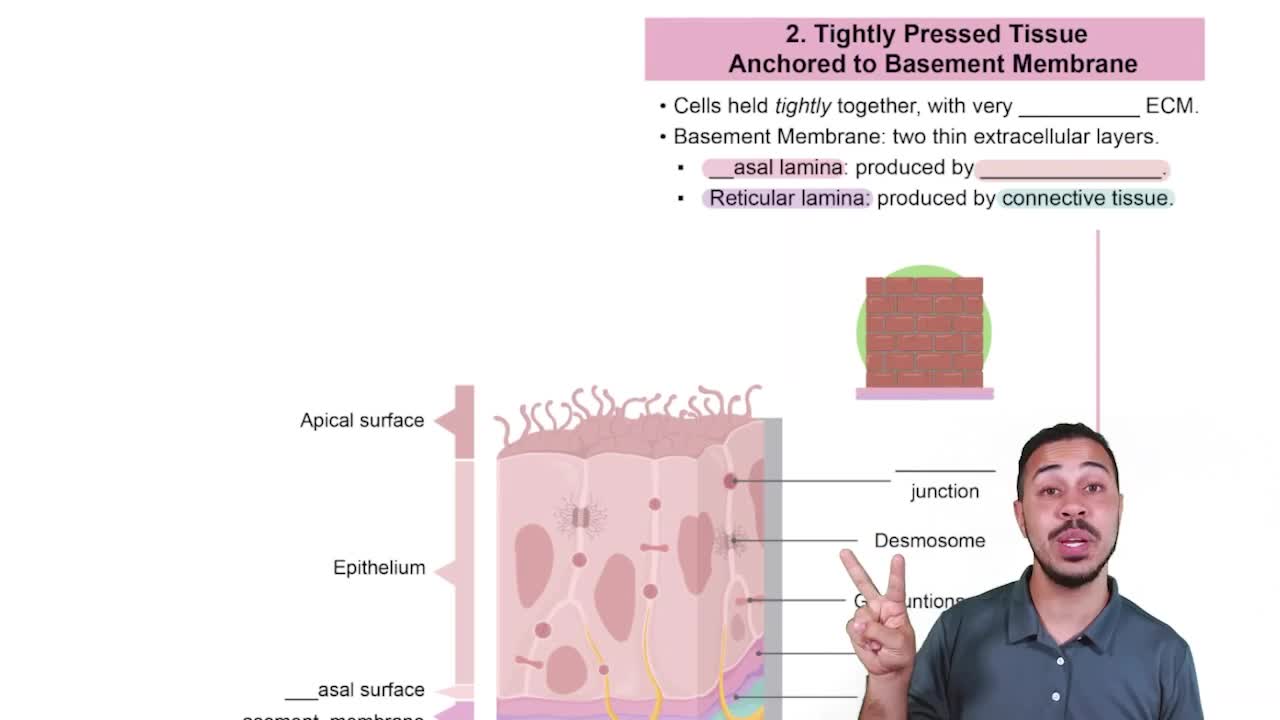
- Basement MembraneExtracellular structure separating epithelial and connective tissues, composed of basal and reticular lamina.
- Tight JunctionsCell junctions creating a leak-proof barrier by holding epithelial cells tightly together.
- DesmosomesComplex cell junctions anchoring neighboring epithelial cells firmly together.
- Gap JunctionsCell junctions allowing exchange of nutrients between neighboring epithelial cells.
- AvascularCharacteristic of epithelial tissue indicating absence of blood vessels.
- InnervatedPresence of nerves in epithelial tissue, enabling sensation detection.
- Connective TissueTissue supporting epithelial tissue by supplying nutrients and removing waste.
- Basal LaminaLayer of the basement membrane produced by epithelial tissue.
- Reticular LaminaLayer of the basement membrane produced by underlying connective tissue.
- Highly RegenerativeEpithelial tissue's ability to rapidly divide and replace damaged cells.
- CancerDisease often originating in epithelial tissue due to rapid cell division and mutation.
- Extracellular MatrixMinimal space between tightly packed epithelial cells, analogous to cement in a brick wall.