Change in Membrane Potential definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackChange in Membrane Potential definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Resting membrane potentialThe state where the inside of a neuron's membrane is negatively charged at -70 millivolts.
- Graded potentialA type of signal resulting from changes in membrane potential, varying in magnitude.
- Action potentialA type of signal resulting from changes in membrane potential, characterized by a rapid rise and fall.
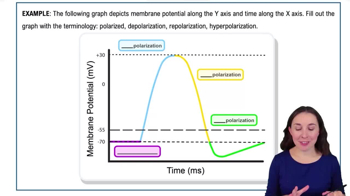
- PolarizedThe state of a neuron when the inside of the membrane is negative, typically at -70 millivolts.
- DepolarizationThe process where the inside of the neuron's membrane becomes more positive, moving away from the resting potential.
- RepolarizationThe process where the inside of the neuron's membrane becomes more negative, returning toward the resting potential.
- HyperpolarizationThe state where the inside of the neuron's membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential.
- Neural communicationThe process by which neurons transmit signals through changes in membrane potential.
- Membrane potentialThe electrical potential difference across a cell's membrane.
- Negative 70 millivoltsThe typical value of the resting membrane potential in neurons.
- Positive 20 millivoltsAn example value used to illustrate depolarization in neurons.
- Temporary decreaseA description of depolarization where membrane potential becomes less negative.
- Temporary increaseA description of hyperpolarization where membrane potential becomes more negative.
- Negative signIndicates a negative charge inside the neuron's membrane during resting potential or repolarization.
- Positive signIndicates a positive charge inside the neuron's membrane during depolarization.