Cells of the Immune System: Granulocytes definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCells of the Immune System: Granulocytes definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
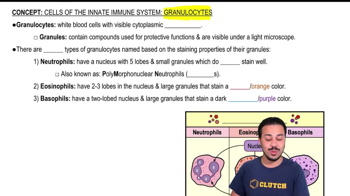
- GranulocytesWhite blood cells with visible cytoplasmic granules, part of the innate immune system.
- NeutrophilsMost abundant leukocytes, first responders to infection, using phagocytosis and degranulation.
- EosinophilsGranulocytes targeting parasitic worms, involved in allergic reactions, with reddish-staining granules.
- BasophilsGranulocytes releasing histamine to promote inflammation, with bluish-purple staining granules.
- LeukocytesWhite blood cells, including granulocytes, crucial for immune defense.
- PhagocytosisProcess of ingesting and digesting microbes or particles by cells like neutrophils.
- DegranulationRelease of granule contents from cells like neutrophils to combat pathogens.
- HistamineMolecule released by basophils and mast cells, increasing capillary permeability during inflammation.
- PolymorphonuclearRefers to cells like neutrophils with a multi-lobed nucleus.
- Antimicrobial peptidesCompounds in neutrophil granules that degrade and destroy microbes.
- Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)Webs of chromatin released by neutrophils to trap and neutralize microbes.
- Capillary permeabilityThe ease with which substances can pass through capillary walls, increased by histamine.
- Mast cellsTissue-resident cells similar to basophils, releasing histamine during allergic reactions.
- Cytoplasmic granulesStructures in granulocytes containing compounds for immune defense, visible under a microscope.
- Innate immune systemThe body's first line of defense, including cells like granulocytes.