Cell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Cell CommunicationThe process by which cells detect and respond to signals in their environment, crucial for immune response.
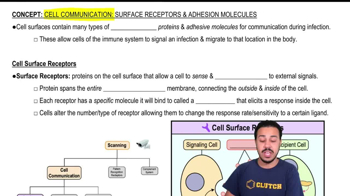
- Surface ReceptorsProteins on the cell membrane that bind to specific ligands, triggering a cellular response.
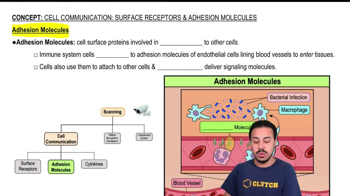
- Adhesion MoleculesCell surface proteins that facilitate binding between cells, aiding immune cell migration.
- LigandA molecule that binds to a specific surface receptor, initiating a cellular response.
- Cytoplasmic MembraneThe cell membrane that surface receptors span, connecting the cell's interior to its exterior.
- Immune SystemThe body's defense system that uses surface receptors and adhesion molecules to combat infections.
- Endothelial CellsCells lining blood vessels that express adhesion molecules to facilitate immune cell migration.
- Cellular ResponseThe reaction within a cell triggered by the binding of a ligand to a surface receptor.
- SignalA molecule or ligand released by a signaling cell to communicate with a recipient cell.
- Recipient CellA cell that has specific surface receptors to detect and respond to a ligand.
- Microbial InfectionAn invasion by microorganisms that the immune system targets using cell communication.
- Blood VesselsStructures lined by endothelial cells where adhesion molecules facilitate immune cell entry.
- MigrationThe movement of immune cells into tissues, enabled by adhesion molecules during infection.
- Innate ImmunityThe body's initial defense mechanism, involving surface receptors and adhesion molecules.
- Signaling MoleculesSubstances delivered by cells to communicate with other cells, often via adhesion molecules.