Cell Communication: Cytokines definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCell Communication: Cytokines definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- CytokinesSoluble proteins that act as communication signals between cells, regulating immune responses and inducing cellular changes.
- ChemokinesCytokines involved in chemotaxis, guiding immune cells to infection sites by signaling movement towards or away from chemical signals.
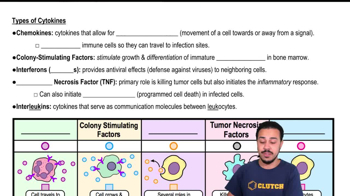
- Colony Stimulating FactorsCytokines that stimulate growth and differentiation of immature leukocytes in the bone marrow.
- InterferonsCytokines providing antiviral defenses to neighboring cells, enhancing their ability to resist viral infections.
- Tumor Necrosis FactorsCytokines that initiate inflammation and can induce apoptosis in infected cells, originally known for killing tumor cells.
- InterleukinsCytokines serving as communication molecules between leukocytes, with diverse functions including promoting inflammation and T cell proliferation.
- IL-1Interleukin that promotes inflammation, fever, and activation of macrophages and T cells.
- IL-2Interleukin that promotes rapid T cell proliferation, enhancing immune response.
- IL-4Interleukin important for promoting antibody immune response, crucial for adaptive immunity.
- IL-6Interleukin that promotes inflammation, fever, and proliferation of T and B cells.
- ChemotaxisProcess involving movement of cells towards or away from chemical signals, guided by chemokines.
- ApoptosisProgrammed cell death initiated by cytokines like tumor necrosis factors in infected cells.
- LeukocytesWhite blood cells involved in immune responses, communication facilitated by interleukins.
- Adaptive ImmunityImmune response involving antibodies, promoted by interleukins like IL-4.
- Phagocytic CellsCells recruited by cytokines to engulf and digest microbes and cellular debris.