ATP definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackATP definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Adenosine TriphosphateA high-energy molecule used to power cellular activities, consisting of adenosine and three phosphate groups.
- Phosphate GroupsThree linked groups in ATP, whose bonds release energy when broken during hydrolysis.
- AdenosineA component of ATP made up of an adenine nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar.
- Pentose SugarA five-carbon sugar that, along with adenine, forms the adenosine part of ATP.
- AdenineA nitrogenous base that pairs with a pentose sugar to form adenosine in ATP.
- ATP HydrolysisThe process of breaking bonds between phosphate groups in ATP, releasing energy.
- Adenosine DiphosphateA molecule formed from ATP hydrolysis, containing two phosphate groups.
- Adenosine MonophosphateA molecule formed from further hydrolysis of ADP, containing one phosphate group.
- Energy CouplingUsing energy from exergonic reactions, like ATP hydrolysis, to drive endergonic reactions.
- Exergonic ReactionA reaction that releases energy, such as ATP hydrolysis.
- Endergonic ReactionA reaction that requires energy input, often driven by ATP hydrolysis.
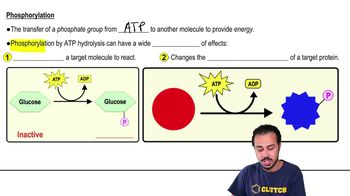
- PhosphorylationThe transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule, altering its activity.
- ActivationA process where phosphorylation makes a molecule reactive or changes its conformation.
- ConformationThe shape or structure of a molecule, which can be altered by phosphorylation.
- Kinetic EnergyEnergy of motion, often derived from ATP hydrolysis in cellular activities.