Antibodies definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackAntibodies definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- AntibodiesY-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells that bind specifically to antigens and generate an immune response.
- ImmunoglobulinsAnother term for antibodies, abbreviated as IG, which are crucial for immune response.
- Plasma cellsCells that produce antibodies as part of the immune response.
- AntigensSubstances that antibodies bind to, triggering an immune response.
- Polypeptide chainsThe four chains (two light, two heavy) that form the structure of an antibody.
- Light chainsThe smaller, lighter polypeptide chains in an antibody, also known as L chains.
- Heavy chainsThe larger, heavier polypeptide chains in an antibody, also known as H chains.
- Disulfide bondsCovalent bonds linking the polypeptide chains in an antibody.
- Variable regionThe part of an antibody that varies between different antibodies and contains the antigen binding site.
- Constant regionThe part of an antibody that remains unchanged across different antibodies.
- FAB regionThe top half of an antibody containing the antigen binding sites.
- FC regionThe bottom half of an antibody containing the constant region.
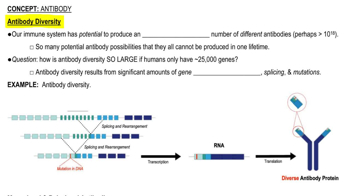
- Gene rearrangementsGenetic processes that contribute to antibody diversity by altering DNA sequences.
- SplicingA process that modifies RNA after transcription, contributing to antibody diversity.
- MutationsChanges in DNA that can lead to the production of diverse antibodies.