Amino Acid Oxidation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackAmino Acid Oxidation definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Urea CycleA liver process converting two nitrogens into one urea molecule, utilizing ATP, to safely excrete nitrogen.
- GlutamineAn amino acid transported from tissues to the liver, converted to glutamate, releasing ammonium for the urea cycle.
- GlutamateFormed from glutamine in the liver, it is converted to alpha-ketoglutarate, releasing ammonium for the urea cycle.
- Alpha-ketoglutarateA product of glutamate dehydrogenation, involved in the release of ammonium for the urea cycle.
- Glucose-Alanine CycleA process where muscles send alanine to the liver, linking amino acid metabolism with gluconeogenesis.
- TransaminasesEnzymes facilitating amino group transfer, indicating tissue damage, especially in liver and heart.
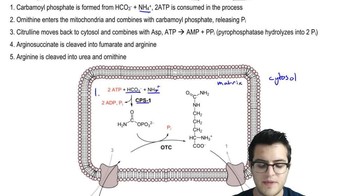
- Carbamoyl PhosphateA molecule formed in the mitochondria, initiating the urea cycle by combining with ornithine.
- OrnithineA molecule entering mitochondria to combine with carbamoyl phosphate, forming citrulline in the urea cycle.
- CitrullineA molecule formed in the urea cycle, exiting mitochondria to combine with aspartate, forming argininosuccinate.
- ArgininosuccinateA molecule in the urea cycle cleaved into fumarate and arginine, linking to the citric acid cycle.
- FumarateA byproduct of the urea cycle, entering the citric acid cycle to be converted into malate and oxaloacetate.
- AspartateFormed from glutamate and oxaloacetate, it combines with citrulline in the urea cycle.
- N-AcetylglutamateA molecule stimulating carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, regulating the urea cycle.
- GlutaminaseAn enzyme converting glutamine to glutamate, releasing ammonium for the urea cycle.
- Glutamate DehydrogenaseAn enzyme converting glutamate to alpha-ketoglutarate, releasing ammonium and reducing NAD+ or NADP+.