Activation Pathways of the Complement System definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackActivation Pathways of the Complement System definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Complement SystemA part of the immune system that enhances the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells.
- Alternative PathwayA complement activation pathway triggered by C3b binding to microbial surfaces, leading to immune responses.
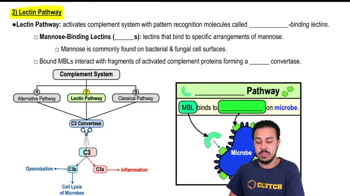
- Lectin PathwayA complement activation pathway using mannose-binding lectins to recognize specific carbohydrate patterns on microbes.
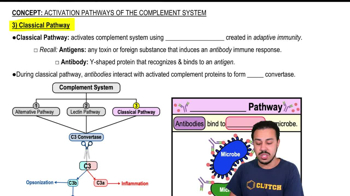
- Classical PathwayA complement activation pathway initiated by antibodies binding to antigens on microbial surfaces.
- C3 ConvertaseAn enzyme complex that cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b, crucial for complement system activation.
- C3aA fragment of C3 that promotes inflammation as part of the immune response.
- C3bA fragment of C3 that binds to microbes, leading to opsonization or cell lysis.
- Mannose-Binding LectinsProteins that bind to mannose on microbial surfaces, initiating the lectin pathway.
- AntibodiesY-shaped proteins produced by adaptive immunity that bind to antigens on microbes.
- AntigensSubstances that induce an immune response, often by binding to antibodies.
- OpsonizationThe process by which pathogens are marked for ingestion and destruction by phagocytes.
- Cell LysisThe breaking down of a cell, often by the rupture of the cell membrane.
- InflammationA biological response to harmful stimuli, characterized by redness, swelling, and pain.
- Innate ImmunityThe non-specific first line of defense against pathogens, including the complement system.
- Adaptive ImmunityThe immune system's ability to recognize and remember specific pathogens for more efficient responses.