11. Nervous Tissue and Nervous System
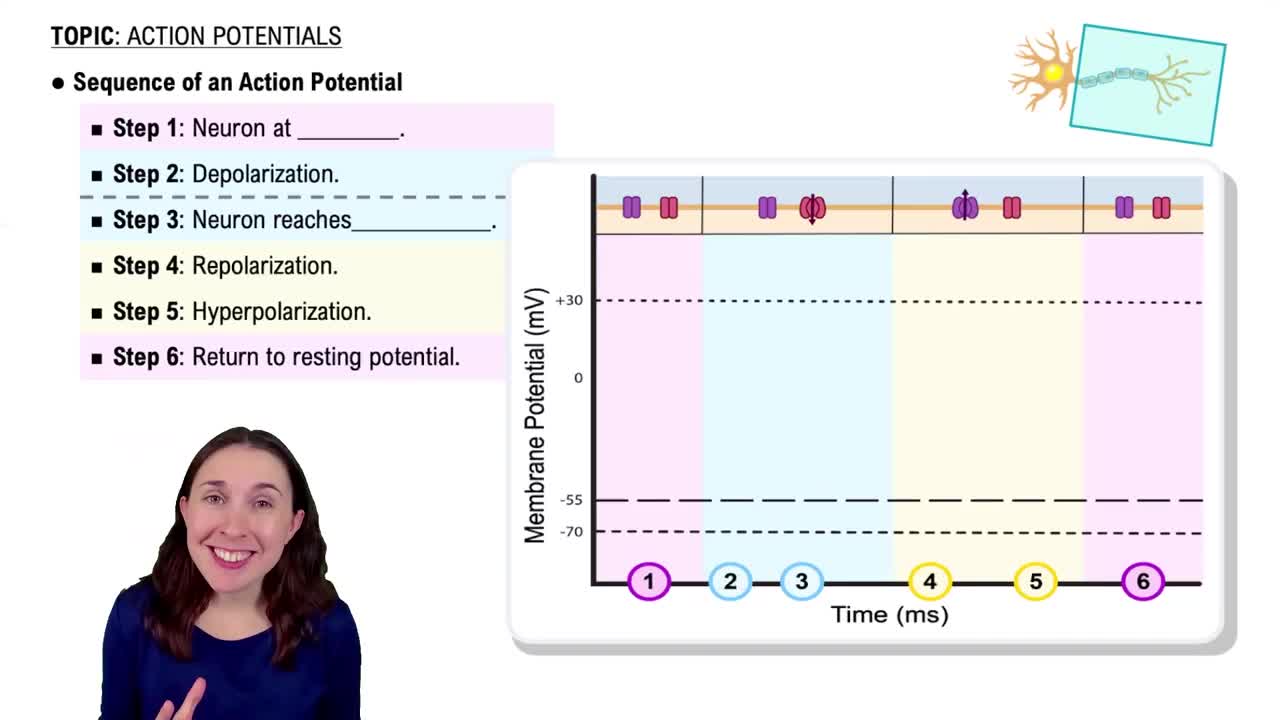
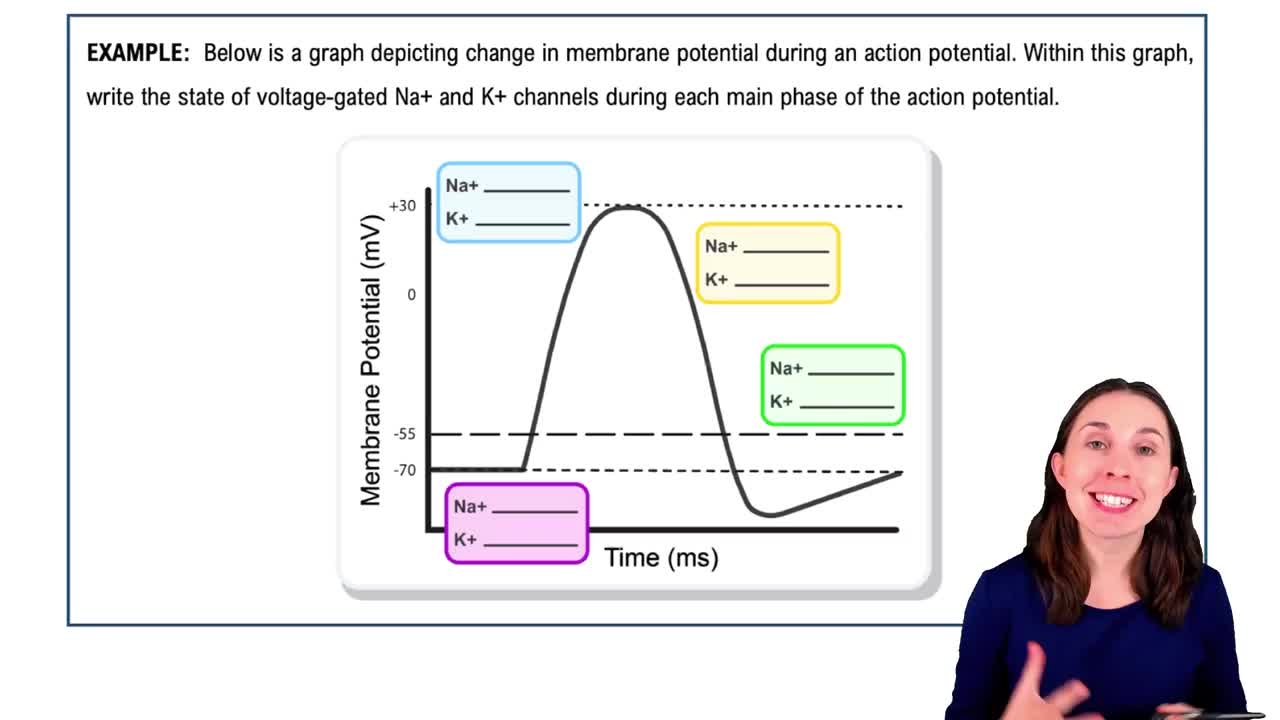
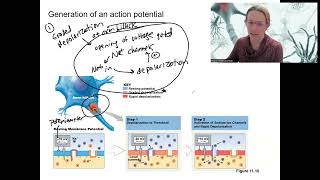
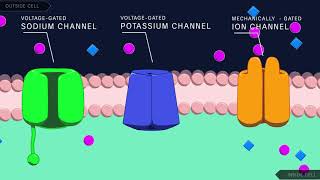
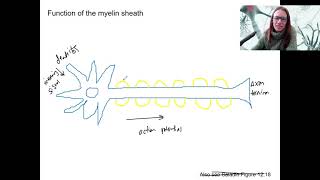
Action Potentials
11. Nervous Tissue and Nervous System
Action Potentials
Additional 7 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 10 of 10 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Casey is taking a new medication that blocks potassium channels. What stage of an action potential would be MOST affected by this drug?
817views26rank - Multiple Choice
When an action potential is at its peak, the electrical gradient forces potassium ____________.
792views15rank - Multiple Choice
What happens when the neuron reaches threshold (-55 mV)?
780views17rank - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following electrical events occurs when a certain threshold is reached?1063views1rank
- Textbook QuestionThe anatomical region of a multipolar neuron where the AP is initiated is the a. soma, b. dendrites, c. axon's initial segment, d. axon terminals.611views1rank
- Textbook QuestionWhat is the polarized membrane state? How is it maintained? (Note the relative roles of both passive and active mechanisms.)464views1rank
- Textbook QuestionDescribe the events that must occur to generate an AP. Relate the sequence of changes in permeability to changes in the ion channels, and explain why the AP is an all-or-none phenomenon.584views1rank
- Textbook QuestionWhen admitted to the emergency room, Sean was holding his right hand, which had a deep puncture hole in its palm. He explained that he had fallen on a nail while exploring a barn. Sean was given an antitetanus shot to prevent neural complications. Tetanus bacteria fester in deep, dark wounds, but how do their toxins travel in neural tissue?485views1rank