2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
Additional 3 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Practice this topic
- Open Question
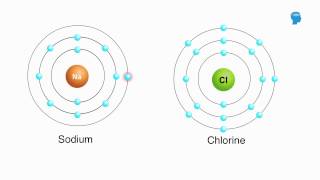
Appropriately label all of the chemical bonds in this image as either intramolecular or intermolecular.
1334views100rank - Multiple Choice
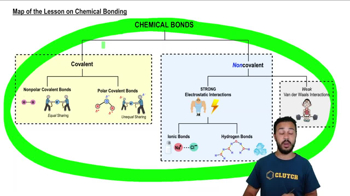
Map of the Lesson on Chemical Bonding
According to the map above, which of the following are types of covalent bonds?
3711views41rank - Multiple ChoiceHow would you respond to this reasoning? Oxygen is not a greenhouse gas; therefore, gases containing oxygen—such as ozone, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide—are not greenhouse gases either.2979views
- Multiple ChoiceAn atom that normally has __________ in its outer shell would not tend to form chemical bonds with other atoms.995views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceThe chemical characteristics or reactivity of an element depend mostly on the __________.1166views
- Open QuestionWhat are the defining characteristics of a condensation reaction? a. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is produced. b. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is used up. c. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is produced. d. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is used up.1855views
- Open QuestionWhat are the defining characteristics of a condensation reaction? a. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is produced. b. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is used up. c. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is produced. d. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is used up.784views
- Textbook QuestionWhat is chemically nonsensical about this structure?801views