6. Bones & Skeletal Tissue
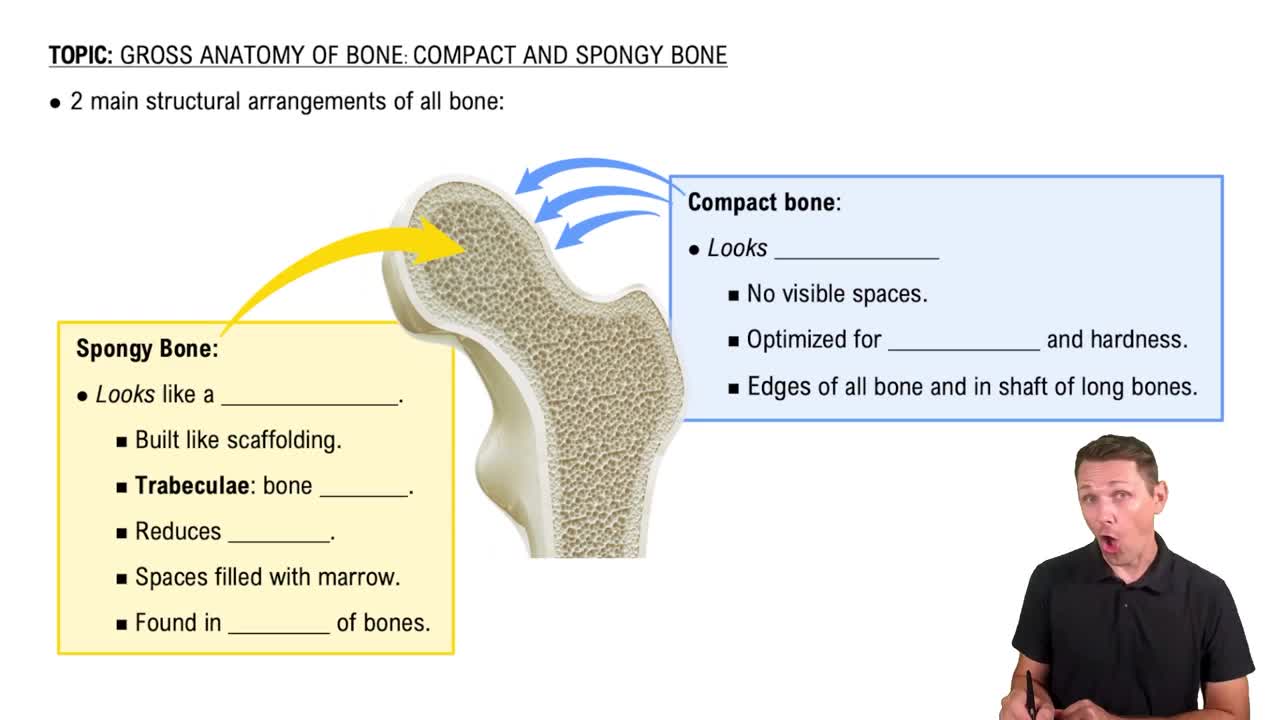
Gross Anatomy of Bone: Compact and Spongy Bone
6. Bones & Skeletal Tissue
Gross Anatomy of Bone: Compact and Spongy Bone
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
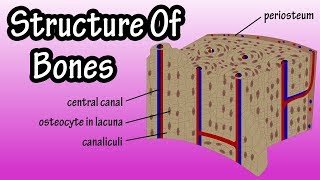
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is a canal-like passageway allowing vasculature and nerves to move through the bone?1654views1comments
- Multiple ChoiceBone is broken down by __________.1058views5rank
- Multiple ChoiceThe cells that maintain mature compact bone are __________.1671views3rank
- Multiple ChoiceOsteocytes maintain contact with the blood vessels of the central canal through __________.1504views1rank
- Textbook Question
Correctly order the following steps of bone growth in length, by placing a 1 by the first step, a 2 by the second step, and so on.
______Calcified cartilage is replaced with bone in the zone of ossification.
______Chondrocytes in the zone of proliferation divide by mitosis.
______Chondrocytes enter the zone of calcification and die as their matrix calcifies.
______Chondrocytes enlarge and cease dividing.
478views2rank - Textbook QuestionYolanda is asked to review a bone slide that her professor has set up under the microscope. She sees concentric layers surrounding a central cavity. Is this bone section taken from the diaphysis or the epiphyseal plate of the specimen?521views1rank
- Textbook QuestionWhat is yellow marrow? How do spongy and compact bone look different?266views
- Textbook QuestionIf spongy bone has no osteons, how do nutrients reach the osteocytes?299views