Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
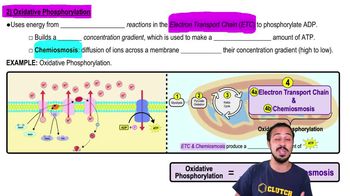
The Electron Transport Chain is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that facilitate the transfer of electrons derived from NADH and FADH2. As electrons move through these complexes, they release energy, which is used to pump protons (H+) from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient essential for ATP synthesis.
Recommended video:
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which ATP is produced using the energy generated from the electron transport chain. The proton gradient created by the ETC drives protons back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase, a process that synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This coupling of electron transport and ATP production is crucial for cellular energy metabolism.
Recommended video:
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Uncoupling Proteins (UCPs)
Uncoupling proteins are a group of mitochondrial transport proteins that disrupt the proton gradient established by the electron transport chain. In brown adipose tissue, UCPs allow protons to re-enter the mitochondrial matrix without passing through ATP synthase, leading to heat production instead of ATP synthesis. This process is vital for thermogenesis, particularly in maintaining body temperature in cold environments.
Recommended video: