Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fermentation Pathway
The fermentation pathway is a metabolic process that allows cells to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. It involves the conversion of glucose into energy-rich compounds, primarily ATP, through anaerobic processes. This pathway is crucial for organisms that live in oxygen-poor environments and relies on the regeneration of NAD+ to sustain glycolysis.
Recommended video:
NADH and NAD+ Interconversion
NADH and NAD+ are coenzymes that play a vital role in cellular metabolism. During fermentation, NADH is oxidized back to NAD+, which is essential for maintaining the flow of glycolysis. This interconversion is critical because it allows the cell to continue producing ATP even when oxygen is not available.
Recommended video:
Electron Carriers: NADH & FADH2
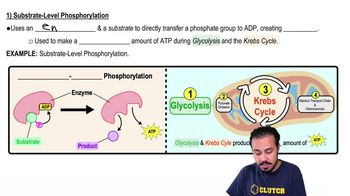
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a method of generating ATP directly from a phosphorylated intermediate during metabolic reactions. In fermentation, this process occurs when a phosphate group is transferred to ADP from a substrate molecule, allowing for ATP synthesis without the need for an electron transport chain, which is typically used in aerobic respiration.
Recommended video:
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution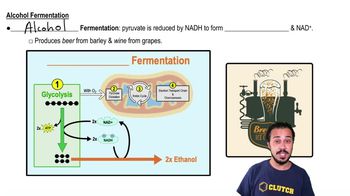


 7:51m
7:51m