Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions, or reduction-oxidation reactions, involve the transfer of electrons between two substances. In these reactions, one reactant undergoes oxidation (loses electrons) while another undergoes reduction (gains electrons). Understanding these processes is crucial for identifying which substances are oxidized and reduced in a chemical equation.
Recommended video:
Combustion of Methane
The combustion of methane (CH4) is a specific type of redox reaction where methane reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). This reaction releases energy in the form of heat and light, making it an exothermic process. Recognizing the products formed helps in determining the changes in oxidation states of the reactants.
Recommended video:
Potential Energy of Bonds
The potential energy of chemical bonds refers to the energy stored in the bonds between atoms. In the context of the combustion of methane, the bonds in methane (CH4) have higher potential energy compared to the bonds in the products (CO2 and H2O). This difference in energy is what drives the reaction, as breaking high-energy bonds releases energy when forming lower-energy products.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution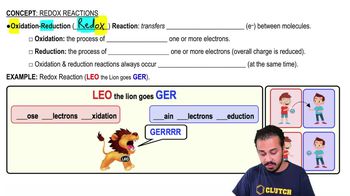



 4:47m
4:47m