Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Proto-oncogenes
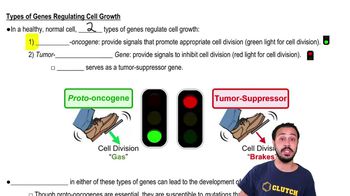
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that play a crucial role in cell growth and division. They encode proteins that help regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. When mutated or abnormally expressed, these genes can become oncogenes, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer. Understanding proto-oncogenes is essential for grasping how cancer can develop from normal cellular processes.
Recommended video:
Types of Genes Regulating Cell Growth
Oncogenes
Oncogenes are mutated forms of proto-oncogenes that promote cancerous growth. They can result from various factors, including genetic mutations, environmental influences, or viral infections. Oncogenes drive the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells by overriding the regulatory mechanisms that control cell division, making their study vital in cancer research and treatment strategies.
Recommended video:
Types of Genes Regulating Cell Growth
Cellular Regulation
Cellular regulation refers to the complex mechanisms that control cell functions, including growth, division, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). This regulation is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and preventing diseases like cancer. The balance between proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes is a key aspect of cellular regulation, as disruptions can lead to the activation of oncogenes and the development of tumors.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution