Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. It consists of several phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, DNA is replicated during the S phase of the cell cycle, and the actual separation of chromosomes occurs during anaphase, where the sister chromatids are pulled apart.
Recommended video:
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a series of phases that a cell goes through to grow and divide. It includes the G1 phase (cell growth), S phase (DNA synthesis), G2 phase (preparation for mitosis), and M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The G1 to G2 transition is crucial for DNA replication, where the amount of DNA in the cell doubles in preparation for mitosis.
Recommended video:
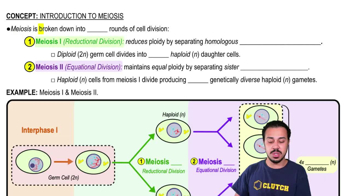
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four non-identical gametes. It consists of two rounds of division: meiosis I and meiosis II. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair and exchange genetic material, but the DNA does not double again between prophase I and prophase II, making it distinct from mitosis.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 8:05m
8:05m