Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that converts glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water. It involves several stages, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, where electrons are transferred through an electron transport chain, generating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Cellular Respiration
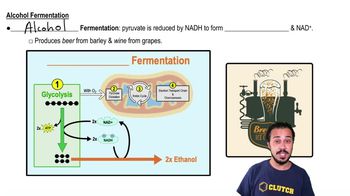
Fermentation
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that allows cells to generate energy without oxygen. It occurs after glycolysis when oxygen is not available, resulting in the conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid or ethanol, depending on the organism. This process yields less ATP compared to cellular respiration but enables continued ATP production in low-oxygen environments.
Recommended video:
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that facilitate the transfer of electrons derived from NADH and FADH2. As electrons move through the chain, they release energy used to pump protons (H+) across the membrane, creating a gradient that drives ATP synthesis via ATP synthase, a key feature of aerobic respiration.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 7:51m
7:51m