Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and Hydrogen Ions
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) present. A lower pH indicates higher acidity, while a higher pH indicates alkalinity. The addition of hydrogen ions to the blood can lower its pH, making it more acidic, which can affect various physiological processes.
Recommended video:
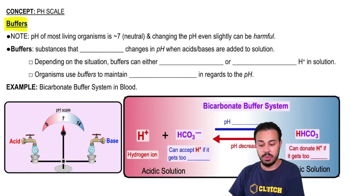
Buffer Systems in Blood
The blood contains buffer systems, primarily bicarbonate, that help maintain a stable pH despite changes in hydrogen ion concentration. These buffers can neutralize excess acids or bases, ensuring that the blood pH remains within a narrow range (7.35-7.45), which is crucial for proper cellular function and overall homeostasis.
Recommended video:
Dietary Impact on Blood pH
While dietary choices can influence the body's acid-base balance, the body has robust mechanisms to regulate blood pH. Foods like citrus are acidic in nature, but their metabolic effects are often neutralized by the body's buffering systems, meaning that consuming acidic foods does not significantly alter blood pH in healthy individuals.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 7:58m
7:58m