Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Epithelial Tissue Classification
Epithelial tissues are classified based on the number of cell layers and the shape of the cells. They can be simple (one layer) or stratified (multiple layers), and the cell shapes can be squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (tall and column-like). Understanding these classifications is essential for identifying specific types of epithelium.
Recommended video:
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
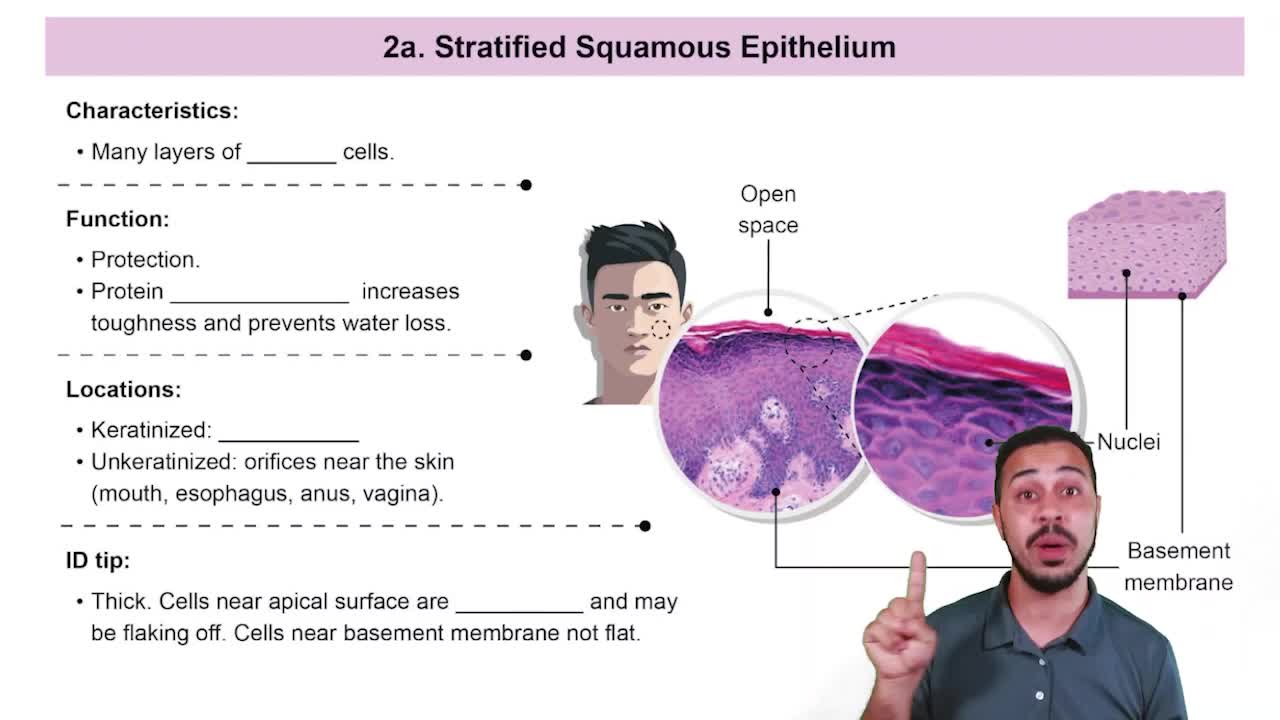
Stratified Epithelium
Stratified epithelium consists of multiple layers of cells, providing protection against abrasion and wear. The apical layer can vary in shape, and in this case, it is specified as flattened cells, indicating that the epithelium is stratified squamous. This type is commonly found in areas subject to friction, such as the skin and the lining of the mouth.
Recommended video:
Stratified Squamous Epithelia
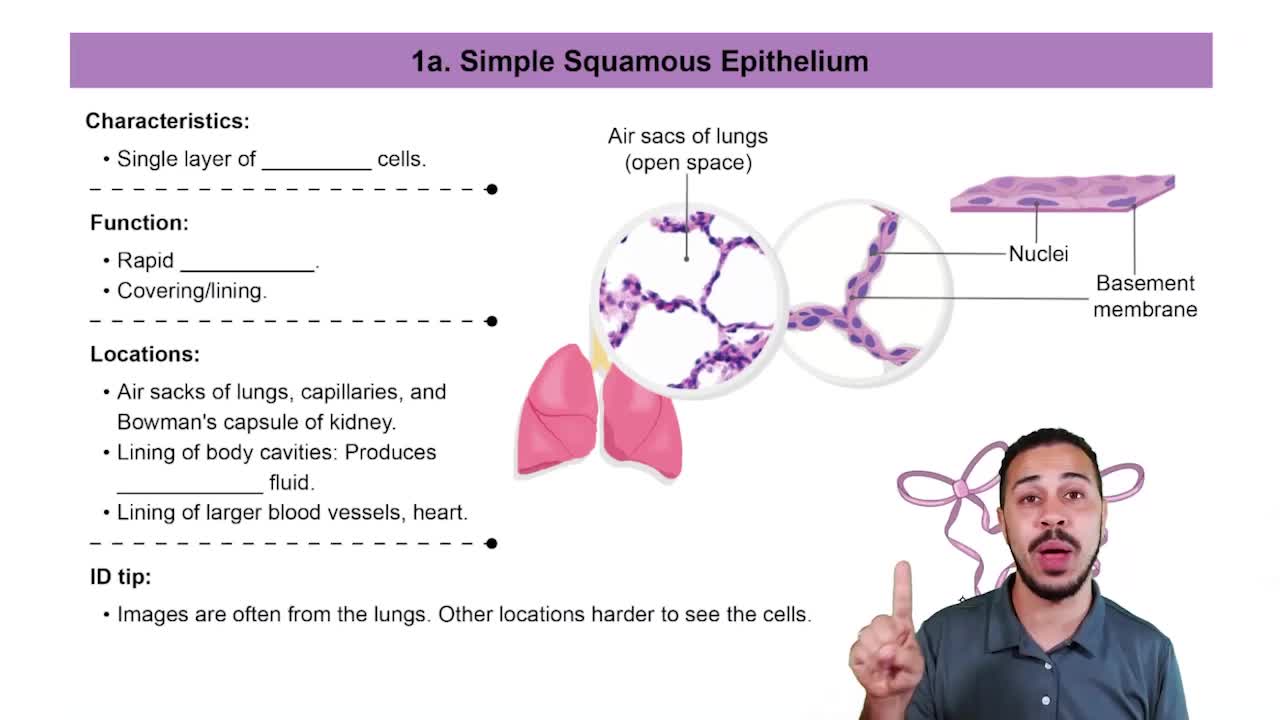
Squamous Cells
Squamous cells are characterized by their flat, scale-like shape. When referring to an epithelium with an apical layer of flattened cells, it indicates that the topmost layer consists of squamous cells. This shape allows for efficient diffusion and filtration, making it ideal for locations like the alveoli of the lungs and the lining of blood vessels.
Recommended video:
Simple Squamous Epithelia
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 4:47m
4:47m