Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are a type of weak chemical bond that occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen, experiences an attraction to another electronegative atom. This interaction is crucial in determining the properties of water, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Recommended video:
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons. In the context of hydrogen bonds, highly electronegative atoms like oxygen and nitrogen create a partial negative charge, which allows them to attract the positively charged hydrogen atoms from other molecules, facilitating bond formation.
Recommended video:
Molecular Polarity
Molecular polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charge across a molecule. Molecules with polar bonds, where there is a significant difference in electronegativity between atoms, can form hydrogen bonds. This polarity is essential for understanding how hydrogen bonds influence the physical properties of substances, such as boiling and melting points.
Recommended video:
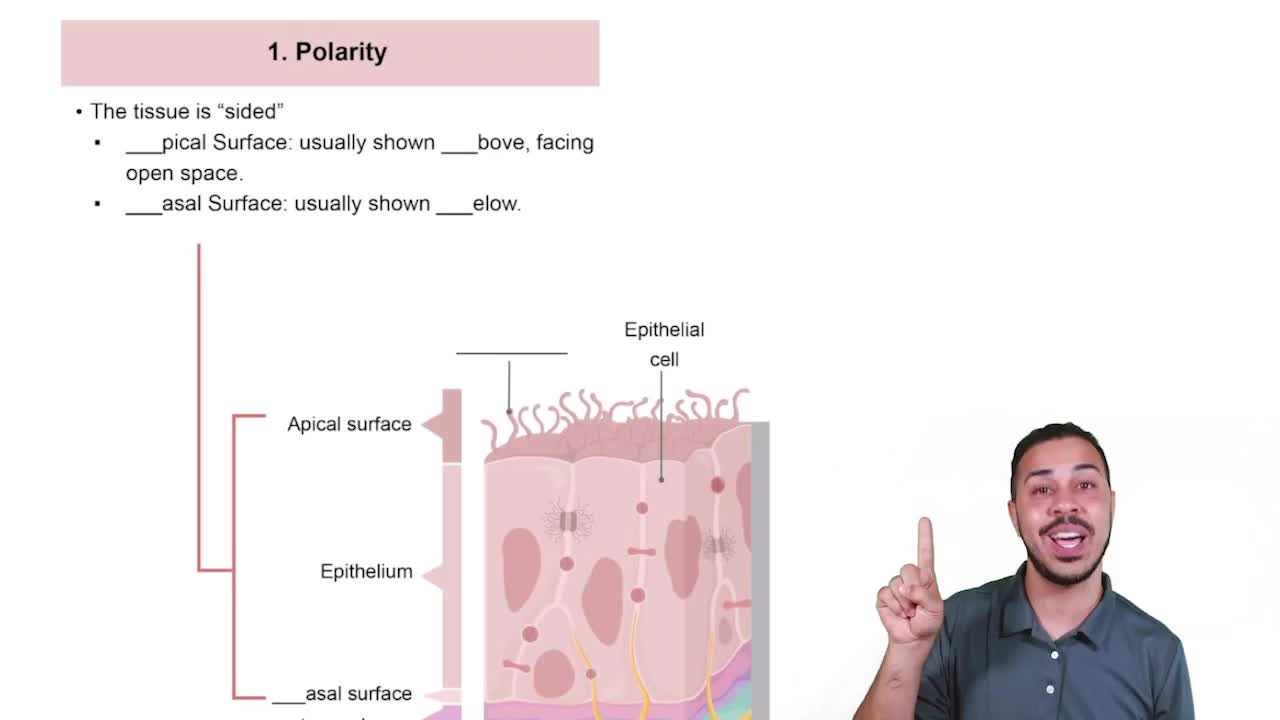
Characteristic 1: Polarity